The SecM arrest peptide traps a pre-peptide bond formation state of the ribosome
- PMID: 38503753
- PMCID: PMC10951299
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46762-2
The SecM arrest peptide traps a pre-peptide bond formation state of the ribosome
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: The SecM arrest peptide traps a pre-peptide bond formation state of the ribosome.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 16;15(1):3276. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47509-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38627409 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
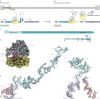
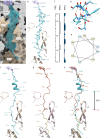
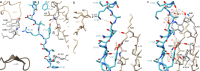
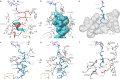
Nascent polypeptide chains can induce translational stalling to regulate gene expression. This is exemplified by the E. coli secretion monitor (SecM) arrest peptide that induces translational stalling to regulate expression of the downstream encoded SecA, an ATPase that co-operates with the SecYEG translocon to facilitate insertion of proteins into or through the cytoplasmic membrane. Here we present the structure of a ribosome stalled during translation of the full-length E. coli SecM arrest peptide at 2.0 Å resolution. The structure reveals that SecM arrests translation by stabilizing the Pro-tRNA in the A-site, but in a manner that prevents peptide bond formation with the SecM-peptidyl-tRNA in the P-site. By employing molecular dynamic simulations, we also provide insight into how a pulling force on the SecM nascent chain can relieve the SecM-mediated translation arrest. Collectively, the mechanisms determined here for SecM arrest and relief are also likely to be applicable for a variety of other arrest peptides that regulate components of the protein localization machinery identified across a wide range of bacteria lineages.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanisms of ribosome stalling by SecM at multiple elongation steps.Elife. 2015 Dec 14;4:e09684. doi: 10.7554/eLife.09684. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26670735 Free PMC article.
-
SecM-stalled ribosomes adopt an altered geometry at the peptidyl transferase center.PLoS Biol. 2011 Jan 18;9(1):e1000581. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000581. PLoS Biol. 2011. PMID: 21267063 Free PMC article.
-
Prolyl-tRNA(Pro) in the A-site of SecM-arrested ribosomes inhibits the recruitment of transfer-messenger RNA.J Biol Chem. 2006 Nov 10;281(45):34258-68. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608052200. Epub 2006 Sep 12. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16968693 Free PMC article.
-
Control of SecA and SecM translation by protein secretion.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004 Apr;7(2):145-50. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2004.01.001. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15063851 Review.
-
Modulating the activity of the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome.RNA. 2008 May;14(5):795-801. doi: 10.1261/rna.980308. Epub 2008 Mar 27. RNA. 2008. PMID: 18369182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RAPP-containing arrest peptides induce translational stalling by short circuiting the ribosomal peptidyltransferase activity.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 19;15(1):2432. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46761-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38503735 Free PMC article.
-
A mini-hairpin shaped nascent peptide blocks translation termination by a distinct mechanism.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 8;16(1):2323. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57659-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40057501 Free PMC article.
-
Are Bacterial Processes Dependent on Global Ribosome Pausing Affected by tRNA Modification Defects?J Mol Biol. 2025 Aug 15;437(16):169107. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2025.169107. Epub 2025 Apr 10. J Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40210524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolving chaperone-assisted protein folding on the ribosome at the peptide level.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024 Dec;31(12):1888-1897. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01355-x. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38987455 Free PMC article.
-
Patchy and widespread distribution of bacterial translation arrest peptides associated with the protein localization machinery.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 2;15(1):2711. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46993-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38565864 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

