Synthetic dual co-stimulation increases the potency of HIT and TCR-targeted cell therapies
- PMID: 38503896
- PMCID: PMC11921049
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-024-00744-x
Synthetic dual co-stimulation increases the potency of HIT and TCR-targeted cell therapies
Abstract
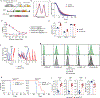
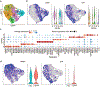
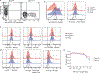
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells have dramatically improved the treatment of hematologic malignancies. T cell antigen receptor (TCR)-based cell therapies are yet to achieve comparable outcomes. Importantly, chimeric antigen receptors not only target selected antigens but also reprogram T cell functions through the co-stimulatory pathways that they engage upon antigen recognition. We show here that a fusion receptor comprising the CD80 ectodomain and the 4-1BB cytoplasmic domain, termed 80BB, acts as both a ligand and a receptor to engage the CD28 and 4-1BB pathways, thereby increasing the antitumor potency of human leukocyte antigen-independent TCR (HIT) receptor- or TCR-engineered T cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Furthermore, 80BB serves as a switch receptor that provides agonistic 4-1BB co-stimulation upon its ligation by the inhibitory CTLA4 molecule. By combining multiple co-stimulatory features in a single antigen-agnostic synthetic receptor, 80BB is a promising tool to sustain CD3-dependent T cell responses in a wide range of targeted immunotherapies.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
Memorial Sloan Kettering has submitted a patent application based in part on results presented in this manuscript (A.D., M.H. and M.S. are listed among the inventors). M.S. reports research funding from Fate Therapeutics, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Atara Biotherapeutics and Mnemo Therapeutics. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



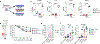





References
Methods Only References
-
- Brentjens RJ et al. Genetically targeted T cells eradicate systemic acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenografts. Clin Cancer Res 13, 5426–5435 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ghani K, Cottin S, de Campos-Lima PO, Caron MC & Caruso M Characterization of an alternative packaging system derived from the cat RD114 retrovirus for gene delivery. J Gene Med 11, 664–669 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Gallardo HF, Tan C, Ory D & Sadelain M Recombinant retroviruses pseudotyped with the vesicular stomatitis virus G glycoprotein mediate both stable gene transfer and pseudotransduction in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Blood 90, 952–957 (1997). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

