RNA-binding proteins potentially regulate the alternative splicing of apoptotic genes during knee osteoarthritis progression
- PMID: 38504181
- PMCID: PMC10949708
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-024-10181-w
RNA-binding proteins potentially regulate the alternative splicing of apoptotic genes during knee osteoarthritis progression
Abstract
Background: Alternative splicing (AS) is a principal mode of genetic regulation and one of the most widely used mechanisms to generate structurally and functionally distinct mRNA and protein variants. Dysregulation of AS may result in aberrant transcription and protein products, leading to the emergence of human diseases. Although considered important for regulating gene expression, genome-wide AS dysregulation, underlying mechanisms, and clinical relevance in knee osteoarthritis (OA) remain unelucidated. Therefore, in this study, we elucidated and validated AS events and their regulatory mechanisms during OA progression.
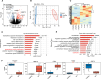
Results: In this study, we identified differentially expressed genes between human OA and healthy meniscus samples. Among them, the OA-associated genes were primarily enriched in biological pathways such as extracellular matrix organization and ossification. The predominant OA-associated regulated AS (RAS) events were found to be involved in apoptosis during OA development. The expression of the apoptosis-related gene BCL2L13, XAF1, and NF2 were significantly different between OA and healthy meniscus samples. The construction of a covariation network of RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and RAS genes revealed that differentially expressed RBP genes LAMA2 and CUL4B may regulate the apoptotic genes XAF1 and BCL2L13 to undergo AS events during OA progression. Finally, RT-qPCR revealed that CUL4B expression was significantly higher in OA meniscus samples than in normal controls and that the AS ratio of XAF1 was significantly different between control and OA samples; these findings were consistent with their expected expression and regulatory relationships.
Conclusions: Differentially expressed RBPs may regulate the AS of apoptotic genes during knee OA progression. XAF1 and its regulator, CUL4B, may serve as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets for this disease.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; Apoptosis; Covariation; Differentially expressed genes; Knee osteoarthritis; RNA binding protein; Transcriptome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



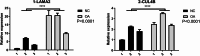
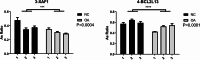
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide analysis revealed the dysregulation of RNA binding protein-correlated alternative splicing events in myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Oct 19;16(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01706-5. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37858115 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of the mRNA expression levels of BCL2 and BAX genes in human osteoarthritis and normal articular cartilage: An investigation into their differential expression.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):4514-4521. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3939. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 26081683
-
Transcriptome-wide analysis reveals the coregulation of RNA-binding proteins and alternative splicing genes in the development of atherosclerosis.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 31;13(1):1764. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26556-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36720950 Free PMC article.
-
RNA binding proteins in osteoarthritis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 8;10:954376. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.954376. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36003144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins regulate osteoarthritis via RNA metabolism regulation.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Dec 28;49(12):1973-1982. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240261. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 40195670 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese, English.
Cited by
-
Get Spliced: Uniting Alternative Splicing and Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 25;25(15):8123. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158123. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

