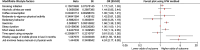Lifestyle factors and subacromial impingement syndrome of the shoulder: potential associations in finnish participants
- PMID: 38504237
- PMCID: PMC10949643
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-024-07345-w
Lifestyle factors and subacromial impingement syndrome of the shoulder: potential associations in finnish participants
Abstract
Background: Emerging evidence has indicated the associations between subacromial impingement syndrome (SIS) of shoulder and lifestyle factors. However, whether unhealthy lifestyle factors causally increase SIS risk is not determined. This study aims to evaluate whether lifestyle factors are the risk factors of SIS.
Methods: A two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) study was designed to evaluate the effect of 11 lifestyle factors on SIS risk. Causality was determined using the inverse-variance weighted method to calculate the odds ratio (OR) and establish a 95% confidence interval (CI). Weighted median method, MR-Egger method and MR-PRESSO method were conducted as sensitivity analysis.
Results: Four lifestyle factors were identified causally associated with an increased risk of SIS using the IVW method: insomnia (OR: 1.66 95% CI 1.38, 2.00; P = 8.86 × 10- 8), short sleep duration (OR: 1.53 95% CI 1.14, 2.05: P = 0.0043), mobile phone usage (OR: 4.65, 95% CI 1.59, 13.64; P = 0.0051), and heavy manual or physical work (OR: 4.24, 95% CI 2.17, 8.26; P = 2.20 × 10- 5). Another causal but weak association was found between smoking initiation on SIS (OR: 1.17, 95% CI 1.01, 1.35; P = 3.50 × 10- 2). Alcohol, coffee consumption, physical activity, sedentary behavior, sleep duration and computer usage were not found to be causally associated with an increased risk of SIS. Sensitivity analyses indicated that the MR estimates were robust and no heterogeneity and pleiotropy were identified in these MR analyses.
Conclusion: Sleep habits and shoulder usage were identified as causal factors for SIS. This evidence supports the development of strategies aimed at improving sleep behaviors and optimizing shoulder usage patterns as effective measures to prevent SIS.
Keywords: Causal effect; Lifestyle factor; Mendelian randomization; Risk; Subacromial impingement syndrome.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exploration of causal relationship between shoulder impingement syndrome and rotator cuff injury: a bidirectional mendelian randomization.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Aug 19;25(1):649. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07556-1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39160499 Free PMC article.
-
Causal effects of body mass index, education, and lifestyle behaviors on intervertebral disc disorders: Mendelian randomization study.J Orthop Res. 2024 Jan;42(1):183-192. doi: 10.1002/jor.25656. Epub 2023 Aug 8. J Orthop Res. 2024. PMID: 37408137
-
Lifestyle factors, metabolic factors and socioeconomic status for pelvic organ prolapse: a Mendelian randomization study.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Jun 7;28(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01148-w. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37287058 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of common lifestyle factors on obstructive sleep apnea: precautions in daily life based on causal inferences.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 5;12:1264082. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1264082. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38504681 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between lifestyle-related risk factors and back pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of Mendelian randomization studies.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Aug 1;25(1):612. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07727-0. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39090551 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetic predisposition to thyrotoxicosis and onset of knee osteoarthritis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Oct 2;15:1364027. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1364027. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39415792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Creech JA, Silver S. Shoulder impingement syndrome. StatPearls. edn. Treasure Island (FL); 2022. - PubMed
-
- Steuri R, Sattelmayer M, Elsig S, Kolly C, Tal A, Taeymans J, Hilfiker R. Effectiveness of conservative interventions including exercise, manual therapy and medical management in adults with shoulder impingement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(18):1340–7. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-096515. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tekeoglu I, Ediz L, Hiz O, Toprak M, Yazmalar L, Karaaslan G. The relationship between shoulder impingement syndrome and sleep quality. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013;17(3):370–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources