Chemical and biosynthetic potential of Penicillium shentong XL-F41
- PMID: 38505237
- PMCID: PMC10949001
- DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.20.52
Chemical and biosynthetic potential of Penicillium shentong XL-F41
Abstract
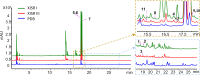
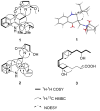
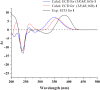
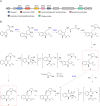
Penicillium strains are renowned for producing diverse secondary metabolites with unique structures and promising bioactivities. Our chemical investigations, accompanied by fermentation media optimization, of a newly isolated fungus, Penicillium shentong XL-F41, led to the isolation of twelve compounds. Among these are two novel indole terpene alkaloids, shentonins A and B (1 and 2), and a new fatty acid 3. Shentonin A (1) is distinguished by an unusual methyl modification at the oxygen atom of the typical succinimide ring, a feature not seen in the structurally similar brocaeloid D. Additionally, shentonin A (1) exhibits a cis relationship between H-3 and H-4, as opposed to the trans configuration in brocaeloid D, suggesting a divergent enzymatic ring-expansion process in their respective fungi. Both shentonins A (1) and B (2) also feature a reduction of a carbonyl to a hydroxy group within the succinimide ring. All isolated compounds were subjected to antimicrobial evaluations, and compound 12 was found to have moderate inhibitory activity against Candia albicans. Moreover, genome sequencing of Penicillium shentong XL-F41 uncovered abundant silent biosynthetic gene clusters, indicating the need for future efforts to activate these clusters and unlock the full chemical potential of the fungus.
Keywords: Penicillium; genome analysis; indole terpene alkaloid; natural products; structure elucidation.
Copyright © 2024, Zou et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ent-homocyclopiamine B, a Prenylated Indole Alkaloid of Biogenetic Interest from the Endophytic Fungus Penicillium concentricum.Molecules. 2019 Jan 9;24(2):218. doi: 10.3390/molecules24020218. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30634398 Free PMC article.
-
Origins, Structures, and Bioactivities of Secondary Metabolites from Marine-derived Penicillium Fungi.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021;21(15):2000-2019. doi: 10.2174/1389557521666210217093517. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33596801
-
Pegriseofamines A-E: Five cyclopiazonic acid related indole alkaloids from the fungus Penicillium griseofulvum.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Jul;136:106553. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106553. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37119783
-
Clavine Alkaloids Gene Clusters of Penicillium and Related Fungi: Evolutionary Combination of Prenyltransferases, Monooxygenases and Dioxygenases.Genes (Basel). 2017 Nov 24;8(12):342. doi: 10.3390/genes8120342. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29186777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Newly reported alkaloids produced by marine-derived Penicillium species (covering 2014-2018).Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jun;99:103840. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103840. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32305696
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
