Patient-specific cutting guides increase accuracy of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy procedure: A retrospective case-control study
- PMID: 38505541
- PMCID: PMC10949175
- DOI: 10.1002/jeo2.12013
Patient-specific cutting guides increase accuracy of medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy procedure: A retrospective case-control study
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the accuracy of patient-specific guides (PSCG) to the standard technique in medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy (OWHTO). Secondary objectives were to evaluate factors that could influence accuracy and to compare the complication rate and operating time for both procedures.
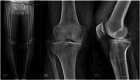
Methods: A retrospective analysis of prospective collected data was performed. Between March 2011 and May 2018, 49 patients with isolated medial knee osteoarthritis who were operated for OWHTO using PSCG and 38 patients using the standard technique were included. Preoperative and postoperative deformities were evaluated on long leg radiographs by measuring the mechanical medial proximal tibial angle, mechanical lateral distal femoral angle, hip knee ankle angle (HKA), and joint line convergence angle. Pre- and postoperative posterior tibial slope was also evaluated. Accuracy was evaluated by analysing the difference between the preoperative planned and the actual postoperative HKA. Operating time and complication rate were also recorded in both groups.
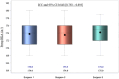
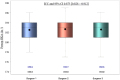
Results: The mean preoperative HKA was 173.4° (±3.1°) in the PSCG group and 173.3° (±2.4°) in the standard group (p = 0.8416). Mean planned HKA were 182.8° (±1.1°) and 184.0° (±0°) respectively for the PSCG and the standard group. Mean postoperative HKA were 181.9° (±1.9°) and 182.6° (±3.1°) respectively for the PSCG and the standard group. An accuracy of ±2° in the HKA was achieved in 44 (90%) in the PSCG group and 24 (65%) in the standard group (p = 0.006). The probability of achieving a HKA accuracy was four times higher for patients in the PSCG group (odds ratio [OR] = 4.06, [1.1; 15.3], p = 0.038). Also, higher preoperative Ahlback grade was associated with precision, all other parameters being equal (OR = 4.2, [0.13; 0.97], p = 0.04).
Conclusion: In this study, the PSCG technique was significantly more accurate for achieving the planned HKA in OWHTO. Complication rates and operating times were comparable between groups.
Level of evidence: Level IV, case-control study.
Keywords: 3D; medial open‐wedge high tibial osteotomy; patient‐specific cutting guide; tibial osteotomy accuracy.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Experimental Orthopaedics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Sports Traumatology, Knee Surgery and Arthroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
One or more of the authors has declared the following potential conflict of interest: Mathieu Thaunat is a paid consultant for, receives research support from, and has made presentations for Arthrex. Jean‐Marie Fayard is a paid consultant, receives research support and has made presentations for Arthrex, NewClip and Xnov. Matthieu Ollivier is a paid consultant, receives research support and has made presentations for Arthrex, NewClip and Stryker. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Can three-dimensional patient-specific cutting guides be used to achieve optimal correction for high tibial osteotomy? Pilot study.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017 Apr;103(2):245-250. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2016.11.020. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 28137553
-
Patient-Specific Cutting Guides for Alignment-Correcting Osteotomy About the Knee: A Study of Accuracy, Cost, and Surgical and Fluoroscopic Safety.Orthop J Sports Med. 2025 Jul 21;13(7):23259671251339497. doi: 10.1177/23259671251339497. eCollection 2025 Jul. Orthop J Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40697812 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of patient-specific cutting guides to lower limb alignment for total knee arthroplasty.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014 Jun;100(4 Suppl):S239-42. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2014.03.006. Epub 2014 Apr 3. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014. PMID: 24703790
-
[Application status of open-wedge high tibial osteotomy assisted by three-dimensional printing patient-specific cutting guides].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023 Mar 15;37(3):360-364. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.202212031. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36940997 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Patient-specific high tibial osteotomy for varus malalignment: 3D-printed plating technique and review of the literature.Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022 Jul;32(5):845-855. doi: 10.1007/s00590-021-03043-8. Epub 2021 Jun 20. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2022. PMID: 34148123 Review.
Cited by
-
Opening wedge high tibial osteotomy using patient-specific instruments and custom-made plates results in accurate correction and improved clinical outcome measures at 1-year follow-up.J Exp Orthop. 2025 Jul 7;12(3):e70340. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70340. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40626186 Free PMC article.
-
The top 100 most-cited knee osteotomy publications.J Exp Orthop. 2025 Apr 1;12(2):e70175. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70175. eCollection 2025 Apr. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40170710 Free PMC article.
-
Digitized Precision Corrective Osteotomy for Treating Knee Joint Deformities: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives.Orthop Surg. 2025 Aug;17(8):2221-2233. doi: 10.1111/os.70085. Epub 2025 May 29. Orthop Surg. 2025. PMID: 40441744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
3D-printed patient-specific instrumentation and the freehand technique in high-tibial osteotomy: A prospective cohort-comparative study in an outpatient setting.J Exp Orthop. 2025 Jan 20;12(1):e70088. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70088. eCollection 2025 Jan. J Exp Orthop. 2025. PMID: 39839856 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Lower Extremity Alignment Correction Using Patient-Specific Cutting Guides and Anatomically Contoured Plates.J Pers Med. 2025 Jul 4;15(7):289. doi: 10.3390/jpm15070289. J Pers Med. 2025. PMID: 40710406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brouwer RW, Bierma‐Zeinstra SMA, van Raaij TM, Verhaar JAN. Osteotomy for medial compartment arthritis of the knee using a closing wedge or an opening wedge controlled by a Puddu plate: a one‐year randomised, controlled study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88‐B(11):1454–1459. 10.1302/0301-620X.88B11.17743 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cerciello S, Ollivier M, Corona K, Kaocoglu B, Seil R. CAS and PSI increase coronal alignment accuracy and reduce outliers when compared to traditional technique of medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy: a meta‐analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;30(2):555–566. 10.1007/s00167-020-06253-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chaouche S, Jacquet C, Fabre‐Aubrespy M, Sharma A, Argenson J‐N, Parratte S, et al. Patient‐specific cutting guides for open‐wedge high tibial osteotomy: safety and accuracy analysis of a hundred patients continuous cohort. Int Orthop. 2019;43(12):2757–2765. 10.1007/s00264-019-04372-4 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

