Case report: Dissolving carotid plaque associated to Lorlatinib-related dyslipidemia
- PMID: 38505589
- PMCID: PMC10949858
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1322501
Case report: Dissolving carotid plaque associated to Lorlatinib-related dyslipidemia
Abstract
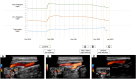
We present a case with prolonged Lorlatinib-related dyslipidemia causing internal carotid artery stenosis, putting the patient at risk of cerebrovascular events. Through intensified lipid-lowering treatment and dose reduction of Lorlatinib, LDL-C levels decreased markedly. Surprisingly, the left sided internal carotid artery stenosis dissolved accordingly. Due to the high efficacy of the new selective tyrosine kinase inhibitors and resulting long-term treatment, it is essential to carefully follow-up and include drug specific side effect monitoring. This case emphasizes that Loraltinib-related dyslipidemia has to be taken seriously and treatment should be initiated as promptly as possible. We conclude that in cases were lipid dysregulation remains and Lorlatinib treatment has to be continued, cerebrovascular appraisal through ultrasound should be considered and, if stenosis is evident, intensified treatment regimen of dyslipidemia or dose reduction of Lorlatinib should be discussed in an interdisciplinary setting.
Keywords: LDL-C; Lorlatinib; case report; dyslipidemia; stroke.
Copyright © 2024 Mayer-Suess, Knoflach, Pircher, Kiechl, Schmidauer and Hametner.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gainor JF, Dardaei L, Yoda S, Friboulet L, Leshchiner I, Katayama R, et al. . Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Discov. (2016) 6:1118–33. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0596 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources