Harnessing the potential of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: from etiology to treatment resistance and clinical applications
- PMID: 38505593
- PMCID: PMC10949897
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1337579
Harnessing the potential of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: from etiology to treatment resistance and clinical applications
Abstract
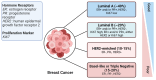
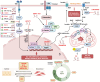
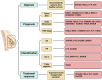
Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignancy among women and a leading cause of cancer-related deaths of females worldwide. It is a complex and molecularly heterogeneous disease, with various subtypes that require different treatment strategies. Despite advances in high-resolution single-cell and multinomial technologies, distant metastasis and therapeutic resistance remain major challenges for BC treatment. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are non-coding RNAs with more than 200 nucleotides in length. They act as competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) to regulate post-transcriptional gene stability and modulate protein-protein, protein-DNA, and protein-RNA interactions to regulate various biological processes. Emerging evidence suggests that lncRNAs play essential roles in human cancers, including BC. In this review, we focus on the roles and mechanisms of lncRNAs in BC progression, metastasis, and treatment resistance, and discuss their potential value as therapeutic targets. Specifically, we summarize how lncRNAs are involved in the initiation and progression of BC, as well as their roles in metastasis and the development of therapeutic resistance. We also recapitulate the potential of lncRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers and discuss their potential use in personalized medicine. Finally, we provide lncRNA-based strategies to promote the prognosis of breast cancer patients in clinical settings, including the development of novel lncRNA-targeted therapies.
Keywords: breast cancer; competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA); liquid biopsy; long non-coding RNA (LncRNA); metastasis; therapy resistance.
Copyright © 2024 Wang, Bu, Luan, Song, Ma, Hao, Yan, Wang, Zheng and Maimaitiyiming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA competing endogenous RNA network identifies four-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer.J Transl Med. 2018 Sep 27;16(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1640-2. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 30261893 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Function of Long Non-coding RNA (LncRNA) Xist.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 10;9:645647. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.645647. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34178980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Drug Resistance of Breast Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 21;13:7075-7087. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S255226. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32764993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA: Dual Effects on Breast Cancer Metastasis and Clinical Applications.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 16;11(11):1802. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111802. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31744046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Long Non-coding RNAs on Bladder Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Aug 4;9:672679. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.672679. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34422802 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Landscape of lncRNAs expressed in Mexican patients with triple‑negative breast cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jun;31(6):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13528. Epub 2025 Apr 11. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40211710 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Modulating the Immune Microenvironment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential.Biomolecules. 2025 Mar 20;15(3):454. doi: 10.3390/biom15030454. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40149989 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

