Unleashing the potential of adipose organoids: A revolutionary approach to combat obesity-related metabolic diseases
- PMID: 38505622
- PMCID: PMC10945346
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.93919
Unleashing the potential of adipose organoids: A revolutionary approach to combat obesity-related metabolic diseases
Abstract
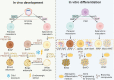
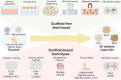
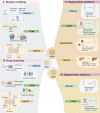
Obesity-related metabolic diseases, including obesity, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases pose a significant threat to health. However, comprehensive pathogenesis exploration and effective therapy development are impeded by the limited availability of human models. Notably, advances in organoid technology enable the generation of adipose organoids that recapitulate structures and functions of native human adipose tissues to investigate mechanisms and develop corresponding treatments for obesity-related metabolic diseases. Here, we review the general principles, sources, and three-dimensional techniques for engineering adipose organoids, along with strategies to promote maturation. We also outline the application of white adipose organoids, primarily for disease modeling and drug screening, and highlight the therapeutic potential of thermogenic beige and brown adipose organoids in promoting weight loss and glucose and lipid metabolic homeostasis. We also discuss the challenges and prospects in the establishment and bench-to-bedside of adipose organoids, as well as their potential applications.
Keywords: Adipose organoid; Brown adipose tissue; Metabolic disease; Obesity; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- González-Muniesa P, Mártinez-González M-A, Hu FB, Després J-P, Matsuzawa Y, Loos RJF. et al. Obesity. Nat Rev Dis Primer. 2017;3:17034. - PubMed
-
- WHO. Obesity and overweight. Revised 9 June 2021. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight.
-
- WHO. World Obesity Day 2022 - Accelerating action to stop obesity. Revised 4 March 2022. https://www.who.int/news/item/04-03-2022-world-obesity-day-2022-accelera....
-
- WHO. Obesity. https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

