Low-Cost Scalable PCB-Based 2-D Transducer Arrays for Volumetric Photoacoustic Imaging
- PMID: 38505656
- PMCID: PMC10947080
- DOI: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3344824
Low-Cost Scalable PCB-Based 2-D Transducer Arrays for Volumetric Photoacoustic Imaging
Abstract
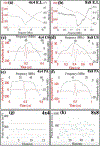
Photoacoustic (PA) imaging provides deep tissue molecular imaging of chromophores with optical absorption contrast and ultrasonic resolution. Present PA imaging techniques are predominantly limited to one 2D plane per acquisition. 2D ultrasound transducers, required for real-time 3D PA imaging, are high-cost, complex to fabricate and have limited scalability in design. We present novel PCB-based 2D matrix ultrasound transducer arrays that are capable of being bulk manufactured at low-cost without using laborious ultrasound fabrication tools. The 2D ultrasound array specifications are easily scalable with respect to widely available PCB design and fabrication tools at low cost. To demonstrate scalability, we fabricated low (11 MHz) frequency 8x8 matrix array and high (40 MHz) frequency 4x4 matrix array by directly bonding an undiced polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) piezoelectric material of desired thickness to the custom designed PCB substrate. Characterization results demonstrate wideband PA receive sensitivity for both low (87%) and high (188%) frequency arrays. Volumetric PA imaging results of light absorbing targets inside optical scattering medium demonstrate improved spatial resolution and field of view with increase in aperture size.
Keywords: 2D Matrix Transducer Array; Beamforming; Photoacoustic Imaging; Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF); Printed Circuit Board (PCB); Ultrasound Transducer Fabrication.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Kothapalli SR, Ma TJ, Vaithilingam S, Oralkan Ö, Khuri-Yakub BT, and Gambhir SS, “Deep tissue photoacoustic imaging using a miniaturized 2-D capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducer array,” IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, vol. 59, no. 5, pp. 1199–1204, May 2012, doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2183593. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
