Worldwide productivity and research trend of publications concerning SIAD: a bibliometric study
- PMID: 38505746
- PMCID: PMC10948503
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1297164
Worldwide productivity and research trend of publications concerning SIAD: a bibliometric study
Abstract
Background: Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic(SIAD) occurs secondary to various diseases, which is characterised by hypotonic hyponatremia and impaired urinary diluting capacity. Research on SIAD in both domestic and international contexts has a long history. This study objectively and comprehensively analyses the research trends, hotspots and development of SIAD research of the past 20 years using the method of bibliometric analysis.
Methods: The 2003-2022 data in the Web of Science Core Collection database were searched. The Bibliometrix software package, VOSviewer and CiteSpace were used to mine, extract and visualise the retrieved literature, and the generated maps were used in analysing the main topics and trends in the field of SIAD research.
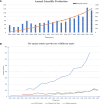
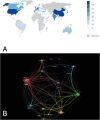
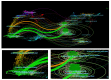
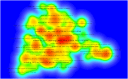
Results: A total of 1215 articles published in 623 journals were included in the analysis, with a total of 18,886 citations. Results showed that the research output on SIAD has continuously increased in the past 20 years, and the United States had the highest number of publications and citations. Keywords with the highest burst strength in recent years were the most mentioned keywords, in addition to the search terms 'hyponatremia', 'covid-19', and 'mortality'. Thus, the relationship among SIAD, covid-19 and mortality may become research frontiers and trends. Fifteen milestone articles were identified through co-citation analysis, which mainly focused on the pathophysiology and treatment of SIAD.
Conclusion: Based on bibliometric analysis and knowledge mapping, this study summarises development trends in the field of SIAD research, providing references for current and future research into SIAD.
Keywords: CiteSpace; SIAD; VOSviewer; bibliometric analysis; development.
Copyright © 2024 Wei, Pan, Lun, Wu, Chen, Feng, Liu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Emerging trends and research foci of oncolytic virotherapy for central nervous system tumors: A bibliometric study.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 6;13:975695. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975695. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36148235 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge mapping of global trends for myasthenia gravis development: A bibliometrics analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 2;14:1132201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1132201. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36936960 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge Structure and Emerging Trends of Telerehabilitation in Recent 20 Years: A Bibliometric Analysis via CiteSpace.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 20;10:904855. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.904855. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35795695 Free PMC article.
-
Publication trends of research on COVID-19 and host immune response: A bibliometric analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Aug 8;10:939053. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.939053. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36003630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of global research trends on male osteoporosis: a neglected field deserves more attention.Arch Osteoporos. 2021 Oct 11;16(1):154. doi: 10.1007/s11657-021-01016-2. Arch Osteoporos. 2021. PMID: 34632530 Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

