Microfluidic techniques for mechanical measurements of biological samples
- PMID: 38505816
- PMCID: PMC10903441
- DOI: 10.1063/5.0130762
Microfluidic techniques for mechanical measurements of biological samples
Abstract
The use of microfluidics to make mechanical property measurements is increasingly common. Fabrication of microfluidic devices has enabled various types of flow control and sensor integration at micrometer length scales to interrogate biological materials. For rheological measurements of biofluids, the small length scales are well suited to reach high rates, and measurements can be made on droplet-sized samples. The control of flow fields, constrictions, and external fields can be used in microfluidics to make mechanical measurements of individual bioparticle properties, often at high sampling rates for high-throughput measurements. Microfluidics also enables the measurement of bio-surfaces, such as the elasticity and permeability properties of layers of cells cultured in microfluidic devices. Recent progress on these topics is reviewed, and future directions are discussed.
© 2022 Public Domain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Figures
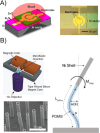
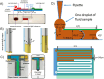

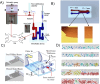


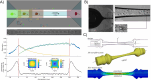

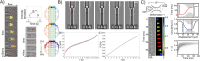

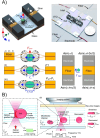
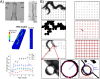


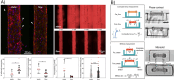
Similar articles
-
Bio-microfluidics: biomaterials and biomimetic designs.Adv Mater. 2010 Jan 12;22(2):249-60. doi: 10.1002/adma.200900821. Adv Mater. 2010. PMID: 20217686
-
Microfluidic Approaches for Microactuators: From Fabrication, Actuation, to Functionalization.Small. 2023 Jun;19(22):e2300469. doi: 10.1002/smll.202300469. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Small. 2023. PMID: 36855777 Review.
-
Materials and methods for droplet microfluidic device fabrication.Lab Chip. 2022 Mar 1;22(5):859-875. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00836f. Lab Chip. 2022. PMID: 35170611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A high-throughput microfluidic device inspired by the Wheatstone bridge principle for characterizing the mechanical properties of single cells.Anal Methods. 2022 Dec 1;14(46):4813-4821. doi: 10.1039/d2ay01416e. Anal Methods. 2022. PMID: 36382629
-
Microfluidics for Biosynthesizing: from Droplets and Vesicles to Artificial Cells.Small. 2020 Mar;16(9):e1903940. doi: 10.1002/smll.201903940. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Small. 2020. PMID: 31603270 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of 3D printed chip to improve sensitivity of platelet adhesion through reinjection: Effect of alcohol consumption on platelet adhesion.Biomicrofluidics. 2025 Jan 3;19(1):014101. doi: 10.1063/5.0237452. eCollection 2025 Jan. Biomicrofluidics. 2025. PMID: 39759388
-
A review of acoustofluidic separation of bioparticles.Biophys Rev. 2023 Aug 29;15(6):2005-2025. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01112-2. eCollection 2023 Dec. Biophys Rev. 2023. PMID: 38192342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing the Mechanical Properties of Rice Cells and Protoplasts under PEG6000 Drought Stress Using Double Resonator Piezoelectric Cytometry.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 9;14(6):303. doi: 10.3390/bios14060303. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38920607 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Blood Viscoelasticity under Microcapillary Blood Flow.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Apr 3;14(4):814. doi: 10.3390/mi14040814. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37421047 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive characterization of oocyte deformability in microconstrictions.Sci Adv. 2025 Feb 21;11(8):eadr9869. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adr9869. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 39970229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Villone M. M. and Maffettone P. L., “ Dynamics, rheology, and applications of elastic deformable particle suspensions: A review,” Rheol. Acta 58, 109 (2019).10.1007/s00397-019-01134-2 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
