A Systems Biology Approach Unveils a Critical Role of DPP4 in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Patient Outcomes
- PMID: 38505912
- PMCID: PMC11419273
- DOI: 10.1615/JEnvironPatholToxicolOncol.2023048056
A Systems Biology Approach Unveils a Critical Role of DPP4 in Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer Patient Outcomes
Abstract
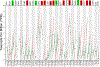
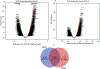
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancers comprise of cancers that affect the digestive system and its accessory organs. The late detection and poor prognosis of GI cancer emphasizes the importance of identifying reliable and precise biomarkers for early diagnosis and prediction of prognosis. The membrane-bound glycoprotein dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP4), also known as CD26, is ubiquitously expressed and has a wide spectrum of biological roles. The role of DPP4/CD26 in tumor progression in different types of cancers remains elusive. However, the link between DPP4 and tumor-infiltrating cells, as well as its prognostic significance in malignancies, still require further investigation. This study was intended to elucidate the correlation of DPP4 expression and survival along with prognosis, followed by its associated enriched molecular pathways and immune cell marker levels in upper GI cancers. Results demonstrated a strong correlation between increased DPP4 expression and a worse prognosis in esophageal and gastric cancer and the co-expressed common genes with DPP4 were associated with crucial molecular pathways involved in tumorigenesis. Additionally, DPP4 was shown to be significantly linked to several immune infiltrating cell marker genes, including Macrophages (M1, M2 and Tumor Associated Macrophages), neutrophils, Treg, T-cell exhaustion, Th1 and Th2. Overall, our findings suggest that DPP4 may serve as a substantial prognostic biomarker, a possible therapeutic target, as well as it can play a critical role in the regulation of immune cell invasion in patients with gastroesophageal (esophageal, gastroesophageal junction and gastric) cancer. KEY WORDS: DPP4, integrated analysis, GI cancer, gastroesophageal cancer, gastroesophageal junction, prognosis.
Figures
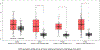
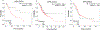
Similar articles
-
Effect of DPP4/CD26 expression on SARS‑CoV‑2 susceptibility, immune response, adenosine (derivatives m62A and CD) regulations on patients with cancer and healthy individuals.Int J Oncol. 2023 Mar;62(3):41. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5489. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36799191 Free PMC article.
-
DPP4/CD26 overexpression in urothelial carcinoma confers an independent prognostic impact and correlates with intrinsic biological aggressiveness.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2995-3008. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13820. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27936466 Free PMC article.
-
CD26/DPP4 - a potential biomarker and target for cancer therapy.Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Jun;198:135-159. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.02.015. Epub 2019 Feb 26. Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30822465 Review.
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV as a Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017 Aug 1;102(8):2930-2940. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-00346. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017. PMID: 28575350
-
DPP4, a potential tumor biomarker, and tumor therapeutic target: review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jan 16;52(1):126. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10235-6. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39821530 Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72(1):7–33. - PubMed
-
- Yamada TADH. Textbook of gastroenterology. Michigan: Wiley-Blackwell Publishing Ltd.; 2009.
-
- Bjelakovic G, Nikolova D, Simonetti RG, Gluud C. Antioxidant supplements for preventing gastrointestinal cancers. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008(3):CD004183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

