Anti-Interleukin-23 Autoantibodies in Adult-Onset Immunodeficiency
- PMID: 38507753
- PMCID: PMC12404335
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2210665
Anti-Interleukin-23 Autoantibodies in Adult-Onset Immunodeficiency
Abstract
Background: Autoantibodies against interleukin-12 (anti-interleukin-12) are often identified in patients with thymoma, but opportunistic infections develop in only some of these patients. Interleukin-12 (with subunits p40 and p35) shares a common subunit with interleukin-23 (subunits p40 and p19). In a patient with disseminated Burkholderia gladioli infection, the identification of both anti-interleukin-23 and anti-interleukin-12 prompted further investigation.
Methods: Among the patients (most of whom had thymoma) who were known to have anti-interleukin-12, we screened for autoantibodies against interleukin-23 (anti-interleukin-23). To validate the potential role of anti-interleukin-23 with respect to opportunistic infection, we tested a second cohort of patients with thymoma as well as patients without either thymoma or known anti-interleukin-12 who had unusual infections.
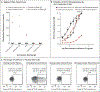
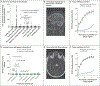
Results: Among 30 patients with anti-interleukin-12 who had severe mycobacterial, bacterial, or fungal infections, 15 (50%) also had autoantibodies that neutralized interleukin-23. The potency of such neutralization was correlated with the severity of these infections. The neutralizing activity of anti-interleukin-12 alone was not associated with infection. In the validation cohort of 91 patients with thymoma, the presence of anti-interleukin-23 was associated with infection status in 74 patients (81%). Overall, neutralizing anti-interleukin-23 was detected in 30 of 116 patients (26%) with thymoma and in 30 of 36 patients (83%) with disseminated, cerebral, or pulmonary infections. Anti-interleukin-23 was present in 6 of 32 patients (19%) with severe intracellular infections and in 2 of 16 patients (12%) with unusual intracranial infections, including Cladophialophora bantiana and Mycobacterium avium complex.
Conclusions: Among patients with a variety of mycobacterial, bacterial, or fungal infections, the presence of neutralizing anti-interleukin-23 was associated with severe, persistent opportunistic infections. (Funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases and others.).
Copyright © 2024 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures


Comment in
-
Anti-Interleukin-23 Autoantibodies in Adult-Onset Immunodeficiency.N Engl J Med. 2024 Jul 11;391(2):187-188. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2404977. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38986069 No abstract available.
-
Anti-Interleukin-23 Autoantibodies in Adult-Onset Immunodeficiency.N Engl J Med. 2024 Jul 11;391(2):188-189. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2404977. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38986070 No abstract available.
-
Anti-Interleukin-23 Autoantibodies in Adult-Onset Immunodeficiency.N Engl J Med. 2024 Jul 11;391(2):189. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2404977. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38986071 No abstract available.
-
Anti-Interleukin-23 Autoantibodies in Adult-Onset Immunodeficiency. Reply.N Engl J Med. 2024 Jul 11;391(2):189-190. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2404977. N Engl J Med. 2024. PMID: 38986072 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
