Targeting of vulnerabilities of drug-tolerant persisters identified through functional genetics delays tumor relapse
- PMID: 38508142
- PMCID: PMC10983104
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101471
Targeting of vulnerabilities of drug-tolerant persisters identified through functional genetics delays tumor relapse
Abstract
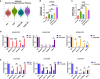
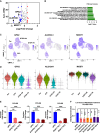
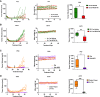
Drug-tolerant persisters (DTPs) are a rare subpopulation of cells within a tumor that can survive therapy through nongenetic adaptive mechanisms to develop relapse and repopulate the tumor following drug withdrawal. Using a cancer cell line with an engineered suicide switch to kill proliferating cells, we perform both genetic screens and compound screens to identify the inhibition of bromodomain and extraterminal domain (BET) proteins as a selective vulnerability of DTPs. BET inhibitors are especially detrimental to DTPs that have reentered the cell cycle (DTEPs) in a broad spectrum of cancer types. Mechanistically, BET inhibition induces lethal levels of ROS through the suppression of redox-regulating genes highly expressed in DTPs, including GPX2, ALDH3A1, and MGST1. In vivo BET inhibitor treatment delays tumor relapse in both melanoma and lung cancer. Our study suggests that combining standard of care therapy with BET inhibitors to eliminate residual persister cells is a promising therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

