Phenotypes and ontogeny of senescent hepatic stellate cells in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
- PMID: 38508241
- PMCID: PMC11269047
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.03.014
Phenotypes and ontogeny of senescent hepatic stellate cells in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Abstract
Background & aims: Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the key drivers of fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), the fastest growing cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) worldwide. HSCs are heterogenous, and a senescent subset of HSCs is implicated in hepatic fibrosis and HCC. Administration of anti-uPAR (urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor) CAR T cells has been shown to deplete senescent HSCs and attenuate fibrosis in murine models. However, the comprehensive features of senescent HSCs in MASH, as well as their cellular ontogeny have not been characterized; hence, we aimed to comprehensively characterize and define the origin of HSCs in human and murine MASH.
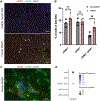
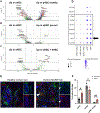
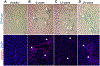
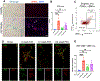
Methods: To comprehensively characterize the phenotype and ontogeny of senescent HSCs in human and murine MASH, we integrated senescence-associated beta galactosidase activity with immunostaining, flow cytometry and single-nucleus RNA sequencing (snRNAseq). We integrated the immunohistochemical profile with a senescence score applied to snRNAseq data to characterize senescent HSCs and mapped the evolution of uPAR expression in MASH.
Results: Using pseudotime trajectory analysis, we establish that senescent HSCs arise from activated HSCs. While uPAR is expressed in MASH, the magnitude and cell-specificity of its expression evolve with disease stage. In early disease, uPAR is more specific to activated and senescent HSCs, while it is also expressed by myeloid-lineage cells, including Trem2+ macrophages and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, in late disease. Furthermore, we identify novel surface proteins expressed on senescent HSCs in human and murine MASH that could be exploited as therapeutic targets.
Conclusions: These data define features of HSC senescence in human and murine MASH, establishing an important blueprint to target these cells as part of future antifibrotic therapies.
Impact and implications: Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are the primary drivers of scarring in chronic liver diseases. As injury develops, a subset of HSCs become senescent; these cells are non-proliferative and pro-inflammatory, thereby contributing to worsening liver injury. Here we show that senescent HSCs are expanded in MASH (metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis) in humans and mice, and we trace their cellular origin from the activated HSC subset. We further characterize expression of uPAR (urokinase plasminogen activated receptor), a protein that marks senescent HSCs, and report that uPAR is also expressed by activated HSCs in early injury, and in immune cells as liver injury advances. We have integrated high-resolution single-nucleus RNA sequencing with immunostaining and flow cytometry to identify five other novel proteins expressed by senescent HSCs, including mannose receptor CD206, which will facilitate future therapeutic development.
Keywords: CD206; hepatic stellate cells; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; senescence; senolytic; uPAR.
Copyright © 2024 European Association for the Study of the Liver. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK056621/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG077921/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R33 CA267221/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA251155/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD033055/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA254838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026880/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK128289/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA078207/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK121154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA045508/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD030463/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK136016/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA129243/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA233944/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG065396/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM146636/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA230636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR004419/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007280/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA283378/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA256480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA196521/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

