Radiotherapy Combined with Intralesional Immunostimulatory Agents for Soft Tissue Sarcomas
- PMID: 38508788
- PMCID: PMC11216412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2024.01.001
Radiotherapy Combined with Intralesional Immunostimulatory Agents for Soft Tissue Sarcomas
Abstract
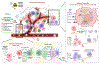
Immunotherapy has shifted the treatment paradigm for many types of cancer. Unfortunately, the most commonly used immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), have yielded limited benefit for most types of soft tissue sarcoma (STS). Radiotherapy (RT) is a mainstay of sarcoma therapy and can induce immune modulatory effects. Combining immunotherapy and RT in STS may be a promising strategy to improve sarcoma response to RT and increase the efficacy of immunotherapy. Most combination strategies have employed immunotherapies, such as ICI, that derepress immune suppressive networks. These have yielded only modest results, possibly due to the limited immune stimulatory effects of RT. Combining RT with immune stimulatory agents has yielded promising preclinical and clinical results but can be limited by the toxic nature of systemic administration of immune stimulants. Using intralesional immune stimulants may generate stronger RT immune modulation and less systemic toxicity, which may be a feasible strategy in accessible tumors such as STS. In this review, we summarize the immune modulatory effects of RT, the mechanism of action of various immune stimulants, including toll-like receptor agonists, and data for combinatorial strategies utilizing these agents.
Copyright © 2024 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest CS, SYK, CXW: Conflicts of interest: none DGK:Grants/Contracts: Stand Up To Cancer (SU2C) Catalyst Research Grant with support from Merck, Xrad Therapeutics, Merck, Varian Medical Systems, Bristol-Myers Squibb. Scientific Advisory Board and Stock Options: Lumicell. Stock ownership: Xrad Therapeutics. AMM: Grants/Contracts: Incyte, Merck, Genentech, BMS, Transgene, EMD Serono, Trisalus. Consulting Fees: Atheneum, First Thought, Opinion Site, Alcimed. Honoraria: ANCO, ACVR. Advisory Board and Stock Options: Multiplex Thera.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Cancer. 2021 Jul;152:165-182. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.04.034. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Eur J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34107450
-
Targeted and immuno-based therapies in sarcoma: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188606. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188606. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34371128 Review.
-
Improving Immunotherapy Efficacy in Soft-Tissue Sarcomas: A Biomarker Driven and Histotype Tailored Review.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 3;12:775761. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.775761. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Immunotherapy in the Management of Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Current Landscape and Future Outlook.J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2022 Jul;20(7):834-844. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2022.7027. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2022. PMID: 35830892 Review.
-
Sarcomas: Immune biomarker expression and checkpoint inhibitor trials.Cancer Treat Rev. 2020 Dec;91:102115. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102115. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020. PMID: 33130422 Review.
Cited by
-
Digitonin-Loaded Nanoscale Metal-Organic Framework for Mitochondria-Targeted Radiotherapy-Radiodynamic Therapy and Disulfidptosis.Adv Mater. 2024 Sep 10:e2405494. doi: 10.1002/adma.202405494. Online ahead of print. Adv Mater. 2024. PMID: 39252688
References
-
- Anagnostou T, Riaz IB, Hashmi SK, et al. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy in acute lymphocytic leukaemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol 7:e816–e826, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Gandhi L, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Gadgeel S, et al. Pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy in metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med 378:2078–2092, 2018 - PubMed

