Nintedanib downregulates the profibrotic M2 phenotype in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages obtained from systemic sclerosis patients affected by interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 38509595
- PMCID: PMC10953168
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-024-03308-7
Nintedanib downregulates the profibrotic M2 phenotype in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages obtained from systemic sclerosis patients affected by interstitial lung disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: Nintedanib downregulates the profibrotic M2 phenotype in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages obtained from systemic sclerosis patients affected by interstitial lung disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Apr 10;26(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03319-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38600545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune connective tissue disease characterized by vasculopathy and progressive fibrosis of skin and several internal organs, including lungs. Macrophages are the main cells involved in the immune-inflammatory damage of skin and lungs, and alternatively activated (M2) macrophages seem to have a profibrotic role through the release of profibrotic cytokines (IL10) and growth factors (TGFβ1). Nintedanib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting several fibrotic mediators and it is approved for the treatment of SSc-related interstitial lung disease (ILD). The study aimed to evaluate the effect of nintedanib in downregulating the profibrotic M2 phenotype in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages (MDMs) obtained from SSc-ILD patients.
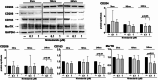
Methods: Fourteen SSc patients, fulfilling the 2013 ACR/EULAR criteria for SSc, 10 SSc patients affected by ILD (SSc-ILD pts), 4 SSc patients non affected by ILD (SSc pts no-ILD), and 5 voluntary healthy subjects (HSs), were recruited at the Division of Clinical Rheumatology-University of Genova, after obtaining Ethical Committee approval and patients' informed consent. Monocytes were isolated from peripheral blood, differentiated into MDMs, and then maintained in growth medium without any treatment (untreated cells), or treated with nintedanib (0.1 and 1µM) for 3, 16, and 24 h. Gene expression of macrophage scavenger receptors (CD204, CD163), mannose receptor-1 (CD206), Mer tyrosine kinase (MerTK), identifying M2 macrophages, together with TGFβ1 and IL10, were evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Protein synthesis was investigated by Western blotting and the level of active TGFβ1 was evaluated by ELISA. Statistical analysis was carried out using non-parametric Wilcoxon test.
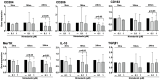
Results: Cultured untreated SSc-ILD MDMs showed a significant increased protein synthesis of CD206 (p < 0.05), CD204, and MerTK (p < 0.01), together with a significant upregulation of the gene expression of MerTK and TGFβ1 (p < 0.05; p < 0.01) compared to HS-MDMs. Moreover, the protein synthesis of CD206 and MerTK and the gene expression of TGFβ1 were significantly higher in cultured untreated MDMs from SSc-ILD pts compared to MDMs without ILD (p < 0.05; p < 0.01). In cultured SSc-ILD MDMs, nintedanib 0.1 and 1µM significantly downregulated the gene expression and protein synthesis of CD204, CD206, CD163 (p < 0.05), and MerTK (p < 0.01) compared to untreated cells after 24 h of treatment. Limited to MerTK and IL10, both nintedanib concentrations significantly downregulated their gene expression already after 16 h of treatment (p < 0.05). In cultured SSc-ILD MDMs, nintedanib 0.1 and 1µM significantly reduced the release of active TGFβ1 after 24 h of treatment (p < 0.05 vs. untreated cells).
Conclusions: In cultured MDMs from SSc-ILD pts, nintedanib seems to downregulate the profibrotic M2 phenotype through the significant reduction of gene expression and protein synthesis of M2 cell surface markers, together with the significant reduction of TGFβ1 release, and notably MerTK, a tyrosine kinase receptor involved in lung fibrosis.
Keywords: Alternatively activated macrophages; Fibrosis; Interstitial lung disease; Systemic sclerosis; Tyrosine kinases inhibitor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MC received a grant provided by Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH for this in vitro study [377835-IT-Collaborative Research Agreement; Study number: 356917]. SS, VS, RC, EG, AC, AS, CP, SP, MC do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prevalence of hybrid TLR4+M2 monocytes/macrophages in peripheral blood and lung of systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 20;15:1488867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1488867. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39635531 Free PMC article.
-
Nintedanib downregulates the transition of cultured systemic sclerosis fibrocytes into myofibroblasts and their pro-fibrotic activity.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Aug 3;23(1):205. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02555-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34344444 Free PMC article.
-
CTLA4-Ig treatment induces M1-M2 shift in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy subjects and rheumatoid arthritis patients.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Dec 24;23(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02691-9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34952630 Free PMC article.
-
Nintedanib: A Review in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases.Drugs. 2021 Apr;81(5):575-586. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01487-0. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33765296 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nintedanib for the treatment of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020 Jun;16(6):547-560. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2020.1777857. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32506975 Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: Nintedanib downregulates the profibrotic M2 phenotype in cultured monocyte-derived macrophages obtained from systemic sclerosis patients affected by interstitial lung disease.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 Apr 10;26(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03319-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38600545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polydatin-curcumin formulation alleviates CTD-ILD-like lung injury in mice via GABBR/PI3K/AKT/TGF-β pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1573525. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1573525. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40538533 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-Like Receptor 8 is Expressed in Monocytes in Contrast to Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Mediates Aberrant Interleukin-10 Responses in Patients With Systemic Sclerosis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025 Jan;77(1):59-66. doi: 10.1002/art.42964. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 39112920 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic macrophage phenotypes in autoimmune and inflammatory rheumatic diseases.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025 Sep;21(9):546-565. doi: 10.1038/s41584-025-01279-w. Epub 2025 Jul 28. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40721670 Review.
-
The Role of Monocytes in the Natural History of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Systematic Literature Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 7;26(13):6538. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136538. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650314 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

