Chemical profiling and arginine kinase inhibitory activity of Angelica dahurica leaves
- PMID: 38509962
- PMCID: PMC10950578
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27589
Chemical profiling and arginine kinase inhibitory activity of Angelica dahurica leaves
Abstract
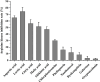
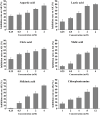
Angelica dahurica is a medicinal herb of the Umbelliferae family. The dried root of A. dahurica, also known as Angelicae dahuricae Radix, is widely used in clinical treatment. However, the aboveground part of A. dahurica which accounted for over 70% of the total plant was abandoned in the field. In order to develop the value of the aboveground part of A. dahurica, the chemical constituents and arginine kinase (AK) inhibitory activity of A. dahurica leaves were studied. 85 volatile components were identified from A. dahurica leaves by GC-MS; 39 non-volatile components including sugars, amino acids and organic acids were identified by pre-column derivatization GC-MS analysis; and 7 coumarins were qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by HPLC. Then, an inhibitory enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (iEIA) was applied for evaluation of AK inhibitory activity. The extracts of A. dahurica leaves exhibited well inhibitory effects on AK. Further, potential AK inhibitors were screened by grey relational analysis and their inhibitory activities were validated by iEIA. l-aspartic acid exhibited strongest inhibitory effect on AK with its IC50 value was 0.558 mM, which was much lower than that of chlorpheniramine (6.644 mM). The obtained chemical profiles displayed chemical diversity of A. dahurica leaves and will provide data support for the future development and utilization of A. dahurica leaves. The screened potential AK inhibitors from A. dahurica leaves could be candidates for development of antiallergic substances or insecticides.
Keywords: Angelica dahurica leaves; Arginine kinase; Chemical composition; Correlation analysis.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Chemical comparison and discrimination of two plant sources of Angelicae dahuricae Radix, Angelica dahurica and Angelica dahurica var. formosana, by HPLC-Q/TOF-MS and quantitative analysis of multiple components by a single marker.Phytochem Anal. 2022 Jul;33(5):776-791. doi: 10.1002/pca.3129. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Phytochem Anal. 2022. PMID: 35470493
-
Mechanisms of improvement of intestinal transport of baicalin and puerarin by extracts of Radix Angelicae Dahuricae.Phytother Res. 2015 Feb;29(2):220-7. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5242. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Phytother Res. 2015. PMID: 25312586
-
[Analysis of volatile constituents and chemical relationship of cultivated and wild Angelica dahurica].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Mar 20;42(3):360-366. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.03.07. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35426799 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The Angelica dahurica: A Review of Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 1;13:896637. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.896637. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35847034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Constituents, Folk Medicinal Uses, and Biological Activities of Genus Angelica: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Dec 28;28(1):267. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010267. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615460 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Commission National Pharmacopoeia . Medical Science and Technology Press; China: 2020. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China.
-
- Tao HJ. Ben Cao Jing Ji Zhu.
-
- Lu F.C. Effect of Angelica dahurica leaves on bee sting. Shandong pharmaceut. ind. 1997;(3):56–57.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

