Outcomes of Reduction Mammaplasty in Adolescents vs Average-Age Patients: A 3-Year Single-Center Retrospective Analysis
- PMID: 38510229
- PMCID: PMC10949056
- DOI: 10.31486/toj.23.0079
Outcomes of Reduction Mammaplasty in Adolescents vs Average-Age Patients: A 3-Year Single-Center Retrospective Analysis
Abstract
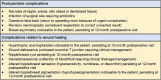
Background: The onset of macromastia symptomatology occurs most often at puberty, yet most females undergo breast reduction surgery during the fifth decade of life. Adolescent patients with macromastia may benefit from reduction mammaplasty, yet outcome data are limited to a small number of institutions. Methods: We conducted a retrospective medical records review of all patients who underwent reduction mammaplasty at our institution during the years 2016 to 2019. Patients were divided into 2 cohorts based on age: adolescent (10 to 24 years) and average age (≥44 years). Demographics and outcome measures were collected from follow-up evaluations at 1-week, 1-month, 3-month, 6-month, and 12-month intervals postoperatively. Results: A total of 141 patients met the inclusion criteria for the study. Mean age at surgery was 19 ± 3.2 years in the adolescent group and 53 ± 7.4 years in the average-age group. No significant differences in complications related to wound healing (42.9% vs 50.0%, P=0.418) or total postoperative complications (18.4% vs 19.6%, P=0.863) were found between adolescent and average-age patients, respectively. Conclusion: Complications related to wound healing are common in reduction mammaplasty, although rates of life-threatening complications are rare. In this 3-year review comparing the outcomes of adolescent vs average-age patients who underwent reduction mammaplasty at the same institution, no significant differences in postoperative complication rates were found. Our data suggest that adolescent patients with macromastia should not defer reduction mammaplasty out of concern for higher complication rates because of age alone.
Keywords: Adolescent; macromastia; mammaplasty.
©2024 by the author(s); Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY).
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comparative Retrospective Analysis of Complications After Oncoplastic Breast Reduction and Breast Reduction for Benign Macromastia: Are These Procedures Equally Safe?Ann Plast Surg. 2015 Oct;75(4):370-5. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000159. Ann Plast Surg. 2015. PMID: 24691307
-
The Effect of Reduction Mammaplasty on Quality of Life in Adolescents With Macromastia.Pediatrics. 2017 Nov;140(5):e20171103. doi: 10.1542/peds.2017-1103. Epub 2017 Oct 6. Pediatrics. 2017. PMID: 28986442
-
Macromastia and Reduction Mammaplasty: Analysis of Outpatient Cost of Care and Opioid Consumption at 5 Years Postoperatively.Aesthet Surg J. 2023 Sep 14;43(10):NP763-NP770. doi: 10.1093/asj/sjad107. Aesthet Surg J. 2023. PMID: 37071801
-
A review of pediatric macromastia etiology and indications for reduction mammaplasty.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2023 Feb;77:209-217. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.12.003. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2023. PMID: 36587475 Review.
-
Breast reduction in adolescents: indication, timing, and a review of the literature.J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2013 Aug;26(4):228-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jpag.2013.03.005. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2013. PMID: 23889919 Review.
Cited by
-
Complications and Satisfaction After Adolescent Breast Reduction for Juvenile Macromastia: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025 Jun 26;13(6):e6913. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006913. eCollection 2025 Jun. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2025. PMID: 40575612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chao JD, Memmel HC, Redding JF, Egan L, Odom LC, Casas LA. Reduction mammaplasty is a functional operation, improving quality of life in symptomatic women: a prospective, single-center breast reduction outcome study. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110(7):1644-1654. - PubMed
-
- Corriveau S, Jacobs JS. Macromastia in adolescence. Clin Plast Surg. 1990;17(1):151-160. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous