Breaking genetic shackles: The advance of base editing in genetic disorder treatment
- PMID: 38510648
- PMCID: PMC10953296
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1364135
Breaking genetic shackles: The advance of base editing in genetic disorder treatment
Abstract
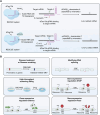
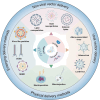
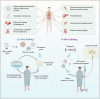
The rapid evolution of gene editing technology has markedly improved the outlook for treating genetic diseases. Base editing, recognized as an exceptionally precise genetic modification tool, is emerging as a focus in the realm of genetic disease therapy. We provide a comprehensive overview of the fundamental principles and delivery methods of cytosine base editors (CBE), adenine base editors (ABE), and RNA base editors, with a particular focus on their applications and recent research advances in the treatment of genetic diseases. We have also explored the potential challenges faced by base editing technology in treatment, including aspects such as targeting specificity, safety, and efficacy, and have enumerated a series of possible solutions to propel the clinical translation of base editing technology. In conclusion, this article not only underscores the present state of base editing technology but also envisions its tremendous potential in the future, providing a novel perspective on the treatment of genetic diseases. It underscores the vast potential of base editing technology in the realm of genetic medicine, providing support for the progression of gene medicine and the development of innovative approaches to genetic disease therapy.
Keywords: adenine base editors; base editing; cytosine base editors; delivery strategies; genetic diseases.
Copyright © 2024 Xu, Zheng, Xu, Zhang, Liu, Chen and Yao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Development of a universal antibiotic resistance screening reporter for improving efficiency of cytosine and adenine base editing.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jul;298(7):102103. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102103. Epub 2022 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35671823 Free PMC article.
-
Base editors: development and applications in biomedicine.Front Med. 2023 Jun;17(3):359-387. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1013-y. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 37434066 Review.
-
[Progress on base editing systems].Yi Chuan. 2019 Sep 20;41(9):777-800. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.19-205. Yi Chuan. 2019. PMID: 31549678 Review. Chinese.
-
Precise in vivo functional analysis of DNA variants with base editing using ACEofBASEs target prediction.Elife. 2022 Apr 4;11:e72124. doi: 10.7554/eLife.72124. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35373735 Free PMC article.
-
[Recent advances and applications of base editing systems].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021 Jul 25;37(7):2307-2321. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200480. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34327897 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Asiaticoside Mitigates Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease by Modulating TRIM27 Stability and Activating PGC-1α/Nrf2 Signaling.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.1007/s12010-025-05288-z. Online ahead of print. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40668528
-
Efficient solid-phase extraction of oligo-DNA from complex media using a nitrocellulose membrane modified with carbon nanotubes and aminated reduced graphene oxide.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 13;15(1):5325. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89705-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39948136 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Diabetic Retinopathy: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Potential.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):9829-9860. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04863-z. Epub 2025 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40164888 Review.
-
A base editing platform for the correction of cancer driver mutations unmasks conserved p53 transcription programs.Genome Biol. 2025 Jul 22;26(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13059-025-03667-7. Genome Biol. 2025. PMID: 40696461 Free PMC article.
-
From bench to bedside: cutting-edge applications of base editing and prime editing in precision medicine.J Transl Med. 2024 Dec 20;22(1):1133. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05957-3. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39707395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

