Loss of Cardiac Splicing Regulator RBM20 Is Associated With Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 38510713
- PMCID: PMC10950405
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2023.08.008
Loss of Cardiac Splicing Regulator RBM20 Is Associated With Early-Onset Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
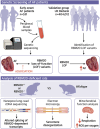
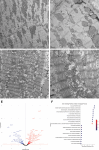
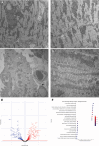
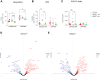
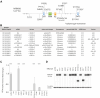
We showed an association between atrial fibrillation and rare loss-of-function (LOF) variants in the cardiac splicing regulator RBM20 in 2 independent cohorts. In a rat model with loss of RBM20, we demonstrated altered splicing of sarcomere genes (NEXN, TTN, TPM1, MYOM1, and LDB3), and differential expression in key cardiac genes. We identified altered sarcomere and mitochondrial structure on electron microscopy imaging and found compromised mitochondrial function. Finally, we demonstrated that 3 novel LOF variants in RBM20, identified in patients with atrial fibrillation, lead to significantly reduced splicing activity. Our results implicate alternative splicing as a novel proarrhythmic mechanism in the atria.
Keywords: RBM20; alternative splicing; atrial cardiomyopathy; atrial fibrillation; genetics.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by the Novo Nordisk Foundation, John and Birthe Meyer Foundation, Research Foundation of the Heart Centre Rigshospitalet, Villadsen Family Foundation, Arvid Nilsson Foundation, Danish Council for Independent Research, Research Foundation at Rigshospitalet, Skibsreder Per Henriksens R., og hustrus fond, and Department of Clinical Medicine (University of Copenhagen). Dr Ahlberg has received a grant from the Novo Nordisk Foundation, BRIDGE–Translational Excellence Programme. Dr Gotthardt was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Leducq Foundation. Dr Svendsen has received a fee for participating in the Advisory Board (Medtronic); and speaker fees from Medtronic not related to this work. Dr Gotthardt has a consultancy agreement with River BioMedics; and has received speaker honoraria from Bayer not related to this work. Dr Olesen has received speaker fees from Biosense Webster not related to this work. All other authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Ahlsson A., Manolis A.S., Casadei B., et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2893–2962. - PubMed
-
- Dobrev D., Nattel S. New antiarrhythmic drugs for treatment of atrial fibrillation. Lancet. 2010;375:1212–1223. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

