Effect of Coca-Cola on the Dissolution of Persimmon-Related Phytobezoar in a Tertiary Care Hospital
- PMID: 38510864
- PMCID: PMC10951130
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.54420
Effect of Coca-Cola on the Dissolution of Persimmon-Related Phytobezoar in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Abstract
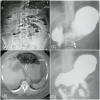
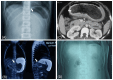
Introduction Bezoars, masses of indigestible foreign bodies formed in the gastrointestinal tract, pose challenges in their management. Phytobezoars are particularly problematic due to their difficult diagnosis and resilience towards treatment. Recently, Coca-Cola has emerged as a potential solution due to its acidic composition and mucolytic properties. However, existing evidence is limited, highlighting the need for comprehensive studies. This research explores the efficacy of Coca-Cola in dissolving persimmon-related phytobezoars, aiming to contribute valuable insights to non-invasive treatment options. Material and methods Conducted as a descriptive case series, this study employed gastric cola lavage using non-probability purposive sampling. Patients aged 18-70 with persimmon-related phytobezoars were included. Two nasogastric tubes were inserted for cola lavage over 12 hours, utilizing three liters of cola until the disappearance of symptoms. When the bezoar disappeared, it was considered as complete success to the treatment. Results Out of 31 patients, 45.2% were male and 54.8% were female, with a mean age of 56.77 ± 9.01 years. Efficacy was noted in 54.8% of cases. Age less than 50 and no history of diabetes mellitus were associated with higher chances of treatment success (p-value ≤0.05). Conclusion Ingestion of Coca-Cola was highly effective, safe, and reliable for the dissolution of persimmon-related phytobezoars, as the frequency of efficacy was high in our study. Coca-Cola ingestion is a non-invasive and cost-effective mode of phytobezoar dissolution that should be taken as a first-line initial treatment option to attain desired outcomes.
Keywords: bezoars; coca–cola; diospyrobezoars; efficacy; gastric bezoars; gastric lavage; persimmon; phytobezoar.
Copyright © 2024, Riaz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Systematic review: Coca-Cola can effectively dissolve gastric phytobezoars as a first-line treatment.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Jan;37(2):169-73. doi: 10.1111/apt.12141. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23252775
-
An Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy Analysis of Elemental Changes of a Persimmon Phytobezoar Dissolved in Coca-Cola.Intern Med. 2016;55(18):2611-5. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.6985. Epub 2016 Sep 15. Intern Med. 2016. PMID: 27629955
-
Gastric and enteric phytobezoars caused by ingestion of persimmon in equids.J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2011 Oct 15;239(8):1110-6. doi: 10.2460/javma.239.8.1110. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2011. PMID: 21985354
-
How good is cola for dissolution of gastric phytobezoars?World J Gastroenterol. 2009 May 14;15(18):2265-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.2265. World J Gastroenterol. 2009. PMID: 19437568 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the diagnosis and management of gastrointestinal bezoars.World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Apr 16;7(4):336-45. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v7.i4.336. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25901212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Temporal changes in computed tomography findings of a persimmon bezoar: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2025 Jun 26;13(18):103426. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i18.103426. World J Clin Cases. 2025. PMID: 40574927 Free PMC article.
-
Gastric Bezoars: A Retrospective Analysis of 44 Cases.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Aug 28;30:e945377. doi: 10.12659/MSM.945377. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39192566 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacobezoars: the challenges of gastric lavage for a patient with drug overdose.World J Emerg Med. 2025;16(2):186-188. doi: 10.5847/wjem.j.1920-8642.2025.025. World J Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 40135210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Gastric phytobezoars may be treated by nasogastric Coca-Cola lavage. Ladas SD, Triantafyllou K, Tzathas C, Tassios P, Rokkas T, Raptis SA. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2002;14:801–803. - PubMed
-
- Two cases of phytobezoars treated by adminsitration of Coca-Cola by oral route. Lee HJ, Kang HG, Park SY, et al. https://www.komci.org/GSResult.php?RID=0028KJG/2006.48.6.431&DT=1. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006;48:431–433. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
