MIAT LncRNA: A multifunctional key player in non-oncological pathological conditions
- PMID: 38511054
- PMCID: PMC10950597
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.01.011
MIAT LncRNA: A multifunctional key player in non-oncological pathological conditions
Abstract
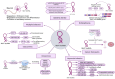
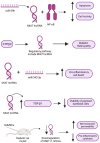
The discovery of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) has unveiled a wide range of transcripts that do not encode proteins but play key roles in several cellular and molecular processes. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are specific class of ncRNAs that are longer than 200 nucleotides and have gained significant attention due to their diverse mechanisms of action and potential involvement in various pathological conditions. In the current review, the authors focus on the role of lncRNAs, specifically highlighting the Myocardial Infarction Associated Transcript (MIAT), in non-oncological context. MIAT is a nuclear lncRNA that has been directly linked to myocardial infarction and is reported to control post-transcriptional processes as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) molecule. It interacts with microRNAs (miRNAs), thereby limiting the translation and expression of their respective target messenger RNA (mRNA) and regulating protein expression. Yet, MIAT has been implicated in other numerous pathological conditions such as other cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune disease, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic diseases, and many others. In this review, the authors emphasize that MIAT exhibits distinct expression patterns and functions across different pathological conditions and is emerging as potential diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic agent. Additionally, the authors highlight the regulatory role of MIAT and shed light on the involvement of lncRNAs and specifically MIAT in various non-oncological pathological conditions.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Disease pathogenesis; LncRNAs; MIAT; Non-oncological conditions; Therapeutic targets.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- El-Aziz M.K.A., et al. Decoding hepatocarcinogenesis from a noncoding RNAs perspective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023;238(9):1982–2009. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

