Sudden cardiac death prevention in the era of novel heart failure medications
- PMID: 38511092
- PMCID: PMC10945958
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ahjo.2023.100281
Sudden cardiac death prevention in the era of novel heart failure medications
Abstract
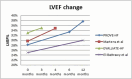
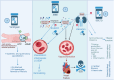
Sudden cardiac death (SCD) occurs unexpectedly and is usually a result of ventricular arrhythmia in patients with structural heart disease. The implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD), with or without biventricular pacing, has been proven to be protective for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction of <35 % (HFrEF). This device therapy prevents SCD, with additional optimal medications, namely angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitors, angiotensin-II receptor-blockers, beta-blockers and mineralocorticoid receptor-antagonists. HFrEF patients present the majority of SCD incidents, as they are characterized by cardiac fibrosis, the main arrhythmogenic element. The introduction of angiotensin-receptor-neprilysin inhibitors, sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and guanylate-cyclase stimulators was associated with reduction of SCD. Additionally, clinical trials have evaluated the improved outcome of these new medications on left ventricular ejection fraction, arrhythmias and HFrEF. These beneficial effects could possibly lead to important changes in decision-making on ICD implantation for primary prevention in patients with HFrEF and reduce the need for device therapy. In this review, we highlight the pathophysiological mechanisms of the new drug agents, and evaluate the possible effect they could have on the role of device therapy as a primary prevention of SCD.
Keywords: Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction; ICD; Sudden cardiac death; Therapy.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Buxton A.E., Calkins H., Callans D.J., DiMarco J.P., Fisher J.D., Greene H.L., et al. ACC/AHA/HRS 2006 key data elements and definitions for electrophysiological studies and procedures: a report of the american College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical data standards (ACC/AHA/HRS writing committee to develop data standards on Electrophysiology) J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006;48(11):2360–2396. - PubMed
-
- Sovari A.A., Karagueuzian H.S. Myocardial fibrosis as a risk stratifier for sudden arrhythmic death. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2011;9(8):951–953. - PubMed
-
- Weiss J.N., Qu Z., Chen P.S., Lin S.F., Karagueuzian H.S., Hayashi H., et al. The dynamics of cardiac fibrillation. Circulation. 2005;112(8):1232–1240. - PubMed
-
- Gräni C., Benz D.C., Gupta S., Windecker S., Kwong R.Y. Sudden Cardiac Death in Ischemic Heart Disease: From Imaging Arrhythmogenic Substrate to Guiding Therapies. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Oct;13(10):2223–2238. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

