Early exercise intervention promotes myelin repair in the brains of ischemic rats by inhibiting the MEK/ERK pathway
- PMID: 38511170
- PMCID: PMC10951688
- DOI: 10.1515/tnsci-2022-0335
Early exercise intervention promotes myelin repair in the brains of ischemic rats by inhibiting the MEK/ERK pathway
Abstract
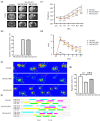
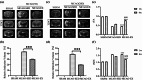
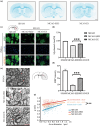
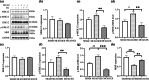
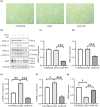
Our previous studies have shown that early exercise intervention after stroke increases neural activity and synaptic plasticity and promotes the recovery of nerve fiber bundle integrity in the brain. However, the effect of exercise on the repair of myelin in the brain and the related mechanism are still unclear. In this study, we randomly divided the rats into three groups. Before and after 28 days of intervention, body weight, nerve function, the infarct size, white matter fiber bundle integrity, and nerve myelin structure and function were observed by measuring body weight, analysis of modified neurological severity score, CatWalk gait analysis, MRI, luxol fast blue staining, immunofluorescence, and transmission electron microscopy. Changes in the expression of proteins in the MEK/ERK pathway were assessed. The results showed that early exercise intervention resulted in neurological recovery, decreased the infarct volume and increased nerve fiber integrity, the myelin coverage area, myelin basic protein (MBP) fluorescence intensity expression, and myelin thickness. Furthermore, the expression level of MBP was significantly increased after early exercise intervention, while the expression levels of p-MEK1/2 and p-ERK1/2 were significantly reduced. In the cell study, MBP expression levels were significantly higher in the oxygen and glucose deprivation and administration group.In summary, early exercise intervention after stroke can promote myelin repair by inhibiting the MEK/ERK signaling pathway.
Keywords: early exercise intervention; middle cerebral artery occlusion; myelin.
© 2024 the author(s), published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treadmill exercise promotes neurogenesis and myelin repair via upregulating Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathways in the juvenile brain following focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion.Int J Mol Med. 2020 May;45(5):1447-1463. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4515. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32323740 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of electroacupuncture on myelin-related protein in corpus callosum of rats with focal cerebral ischemia].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021 Sep 25;46(9):721-7. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210187. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021. PMID: 34558236 Chinese.
-
Buyang huanwu decoction improves synaptic plasticity of ischemic stroke by regulating the cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;335:118636. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118636. Epub 2024 Jul 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39089658
-
TREM2 mediates physical exercise-promoted neural functional recovery in rats with ischemic stroke via microglia-promoted white matter repair.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Feb 25;20(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02741-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36829205 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise Intervention Promotes the Growth of Synapses and Regulates Neuroplasticity in Rats With Ischemic Stroke Through Exosomes.Front Neurol. 2021 Oct 28;12:752595. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.752595. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34777222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han P, Zhang W, Kang L, Ma Y, Fu L, Jia L, et al. Clinical evidence of exercise benefits for stroke. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1000:131–51. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
