Efficient and economic protein labeling for NMR in mammalian expression systems: Application to a preT-cell and T-cell receptor protein
- PMID: 38511503
- PMCID: PMC10955624
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4950
Efficient and economic protein labeling for NMR in mammalian expression systems: Application to a preT-cell and T-cell receptor protein
Abstract
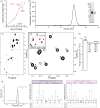
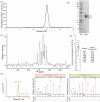
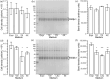
Protein nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy relies on the ability to isotopically label polypeptides, which is achieved through heterologous expression in various host organisms. Most commonly, Escherichia coli is employed by leveraging isotopically substituted ammonium and glucose to uniformly label proteins with 15N and 13C, respectively. Moreover, E. coli can grow and express proteins in uniformly deuterium-substituted water (D2O), a strategy useful for experiments targeting high molecular weight proteins. Unfortunately, many proteins, particularly those requiring specific posttranslational modifications like disulfide bonding or glycosylation for proper folding and/or function, cannot be readily expressed in their functional forms using E. coli-based expression systems. One such class of proteins includes T-cell receptors and their related preT-cell receptors. In this study, we present an expression system for isotopic labeling of proteins using a nonadherent human embryonic kidney cell line, Expi293F, and a specially designed media. We demonstrate the application of this platform to the β subunit common to both receptors. In addition, we show that this expression system and media can be used to specifically label amino acids Phe, Ile, Val, and Leu in this system, utilizing an amino acid-specific labeling protocol that allows targeted incorporation at high efficiency without significant isotopic scrambling. We demonstrate that this system can also be used to express proteins with fluorinated amino acids. We were routinely able to obtain an NMR sample with a concentration of 200 μM from 30 mL of culture media, utilizing less than 20 mg of the labeled amino acids.
Keywords: 19F‐labeling; Expi293F; T‐cell receptor (TCR); glycosylation; local deuteration; mammalian expression; methyl TROSY; nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR); preT‐cell receptor (preTCR).
© 2024 The Protein Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Arjen van den Berg, Jonathan Zmuda, and Melissa Cross are employed by Thermo Fisher. Vladimir Gelev is the founder of FB Reagents Ltd., a company specializing in stable isotope‐labeled biochemicals. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


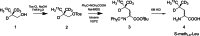
Similar articles
-
Differential isotope-labeling for Leu and Val residues in a protein by E. coli cellular expression using stereo-specifically methyl labeled amino acids.J Biomol NMR. 2013 Nov;57(3):237-49. doi: 10.1007/s10858-013-9784-0. Epub 2013 Sep 21. J Biomol NMR. 2013. PMID: 24057411
-
Improving yields of deuterated, methyl labeled protein by growing in H2O.J Biomol NMR. 2018 Aug;71(4):263-273. doi: 10.1007/s10858-018-0200-7. Epub 2018 Aug 2. J Biomol NMR. 2018. PMID: 30073492 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 13C-methyl-labeled amino acids and their incorporation into proteins in mammalian cells.Org Biomol Chem. 2023 Nov 29;21(46):9216-9229. doi: 10.1039/d3ob01320k. Org Biomol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37964666 Free PMC article.
-
Selective labeling and unlabeling strategies in protein solid-state NMR spectroscopy.J Biomol NMR. 2018 Jul;71(3):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s10858-017-0156-z. Epub 2017 Dec 2. J Biomol NMR. 2018. PMID: 29197975 Review.
-
Mammalian expression of isotopically labeled proteins for NMR spectroscopy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;992:197-211. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-4954-2_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 23076586 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

