No immunological interference or concerns about safety when seasonal quadrivalent influenza vaccine is co-administered with a COVID-19 mRNA-1273 booster vaccine in adults: A randomized trial
- PMID: 38513689
- PMCID: PMC10962584
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2327736
No immunological interference or concerns about safety when seasonal quadrivalent influenza vaccine is co-administered with a COVID-19 mRNA-1273 booster vaccine in adults: A randomized trial
Abstract
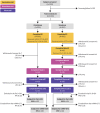
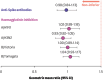
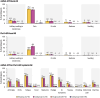
The objective of the study was to assess the safety and immunogenicity of mRNA-1273 COVID-19 booster vaccination when co-administered with an egg-based standard dose seasonal quadrivalent influenza vaccine (QIV). This was a phase 3, randomized, open-label study. Eligible adults aged ≥ 18 years were randomly assigned (1:1) to receive mRNA-1273 (50 µg) booster vaccination and QIV 2 weeks apart (Seq group) or concomitantly (Coad group). Primary objectives were non-inferiority of haemagglutinin inhibition (HI) and anti-Spike protein antibody responses in the Coad compared to Seq group. 497/498 participants were randomized and vaccinated in the Seq/Coad groups, respectively. The adjusted geometric mean titer/concentration ratios (95% confidence intervals) (Seq/Coad) for HI antibodies were 1.02 (0.89-1.18) for A/H1N1, 0.93 (0.82-1.05) for A/H3N2, 1.00 (0.89-1.14] for B/Victoria, and 1.04 (0.93-1.17) for B/Yamagata; and 0.98 (0.84-1.13) for anti-Spike antibodies, thus meeting the protocol-specified non-inferiority criteria. The most frequently reported adverse events in both groups were pain at the injection site and myalgia. The 2 groups were similar in terms of the overall frequency, intensity, and duration of adverse events. In conclusion, co-administration of mRNA-1273 booster vaccine with QIV in adults was immunologically non-inferior to sequential administration. Safety and reactogenicity profiles were similar in both groups (clinicaltrials.gov NCT05047770).
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccine; Co-administration; immunogenicity; influenza vaccine; mRNA-1273.
Plain language summary
What is the context? Updated booster shots against COVID-19 disease are likely to offer more protection as the virus is changing over time.It is important for doctors, other healthcare providers and patients to know whether COVID-19 booster vaccines can be given at the same time as other vaccines recommended for adults.What is new? The results of our study showed that an mRNA-based COVID-19 booster vaccine could be given at the same time as the seasonal influenza vaccine.When given together, both vaccines led to immune responses and had side effects that were similar to those observed when they were given at separate times.What is the impact? The potential benefits of administering more than 1 vaccine during a healthcare visit include improved coverage and a reduced number of doctor visits needed to receive all vaccines.Co-administration of COVID-19 booster vaccines and influenza vaccines could be an attractive option for patients and healthcare professionals.
Conflict of interest statement
Abdi Naficy is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. Adrienne Kuxhausen is employed by GSK. Harry Seifert is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. Andrew Hastie is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. Brett Leav is employed by Moderna and holds shares in Moderna. Jacqueline Miller was employed by the GSK until May 2020 and is now employed by Moderna. Jacqueline Miller also reports she holds shares in GSK and Moderna. Kate Anteyi is employed by Moderna and holds shares in Moderna. Agnes Mwakingwe-Omari is employed by GSK and holds shares in GSK. All authors declare no other financial and non-financial relationships and activities or conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Feikin DR, Higdon MM, Abu-Raddad LJ, Andrews N, Araos R, Goldberg Y, Groome MJ, Huppert A, O’Brien KL, Smith PG, et al. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: results of a systematic review and meta-regression. The Lancet. 2022;399:924–10. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00152-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- VRBPAC. Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee Meeting . Selection of strain(s) to be included in the periodic updated COVID-19 vaccines for the 2023–2024 vaccination campaign; 2023. Jun 15 [accessed 2023 Jun 21]. https://www.fda.gov/media/169538/download.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
