Optimized machine learning model for air quality index prediction in major cities in India
- PMID: 38514669
- PMCID: PMC10958024
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-54807-1
Optimized machine learning model for air quality index prediction in major cities in India
Abstract
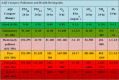
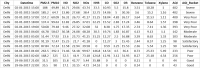
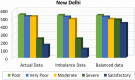
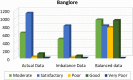
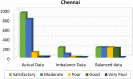
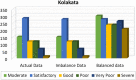
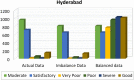
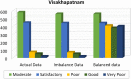
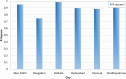
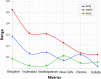
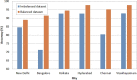
Industrial advancements and utilization of large amount of fossil fuels, vehicle pollution, and other calamities increases the Air Quality Index (AQI) of major cities in a drastic manner. Major cities AQI analysis is essential so that the government can take proper preventive, proactive measures to reduce air pollution. This research incorporates artificial intelligence in AQI prediction based on air pollution data. An optimized machine learning model which combines Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) with the Decision Tree (DT) algorithm for accurate prediction of AQI in major cities of India. Air quality data available in the Kaggle repository is used for experimentation, and major cities like Delhi, Hyderabad, Kolkata, Bangalore, Visakhapatnam, and Chennai are considered for analysis. The proposed model performance is experimentally verified through metrics like R-Square, RMSE, MSE, MAE, and accuracy. Existing machine learning models, like k-nearest Neighbor, Random Forest regressor, and Support vector regressor, are compared with the proposed model. The proposed model attains better prediction performance compared to traditional machine learning algorithms with maximum accuracy of 88.98% for New Delhi city, 91.49% for Bangalore city, 94.48% for Kolkata, 97.66% for Hyderabad, 95.22% for Chennai and 97.68% for Visakhapatnam city.
Keywords: Air pollution; Air quality index; Decision tree regression; Grey-wolf optimization; Machine learning; Optimization algorithm.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Evaluation of machine learning and deep learning models for daily air quality index prediction in Delhi city, India.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Nov 19;196(12):1215. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13351-1. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39557698
-
Air quality prediction by machine learning models: A predictive study on the indian coastal city of Visakhapatnam.Chemosphere. 2023 Oct;338:139518. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139518. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Chemosphere. 2023. PMID: 37454985
-
Air pollution particulate matter (PM2.5) prediction in South African cities using machine learning techniques.Front Artif Intell. 2023 Oct 10;6:1230087. doi: 10.3389/frai.2023.1230087. eCollection 2023. Front Artif Intell. 2023. PMID: 37881653 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of air pollutants on climate change and prediction of air quality index using machine learning models.Environ Res. 2023 Dec 15;239(Pt 1):117354. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2023.117354. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 37821071
-
Performance analysis of machine learning models for AQI prediction in Gorakhpur City: a critical study.Environ Monit Assess. 2024 Sep 12;196(10):924. doi: 10.1007/s10661-024-13107-x. Environ Monit Assess. 2024. PMID: 39264506
Cited by
-
Advanced air quality prediction using multimodal data and dynamic modeling techniques.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 30;15(1):27867. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11039-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40738914 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring PM2.5 and PM10 ML forecasting models: a comparative study in the UAE.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9797. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-94013-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40118896 Free PMC article.
-
Explainable forecasting of air quality index using a hybrid random forest and ARIMA model.MethodsX. 2025 Jul 18;15:103517. doi: 10.1016/j.mex.2025.103517. eCollection 2025 Dec. MethodsX. 2025. PMID: 40777582 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced air quality prediction using adaptive residual Bi-LSTM with pyramid dilation and optimal weighted feature selection.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 19;15(1):30428. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14668-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40830158 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient multi-station air quality prediction in Delhi with wavelet and optimization-based models.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 19;20(8):e0330465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330465. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40828857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yuan Y, Yang Q, Ren J, Fan J, Shen Q, Wang X, Zhao Y. Learning-imitation strategy-assisted alpine skiing optimization for the boom of offshore drilling platform. Ocean Eng. 2023;278:114317. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.114317. - DOI
-
- Yuan Y, Wang S, Lv L, Song X. An adaptive resistance and stamina strategy-based dragonfly algorithm for solving engineering optimization problems. Eng. Comput. 2022;38(5):2228–2251. doi: 10.1108/EC-08-2019-0362. - DOI
-
- Yuan Y, Xiaokai Mu, Shao X, Ren J, Zhao Y, Wang Z. Optimization of an auto drum fashioned brake using the elite opposition-based learning and chaotic k-best gravitational search strategy based grey wolf optimizer algorithm. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022;123:10897. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2022.108947. - DOI
-
- Gladkova E, Saychenko L. Applying machine learning techniques in air quality prediction. Transport. Res. Proc. 2022;63:1999–2006. doi: 10.1016/j.trpro.2022.06.222. - DOI
-
- Zhou Y, De S, Ewa G, Perera C, Moessner K. Data-driven air quality characterization for urban environments: A case study. IEEE Access. 2018;6:77996–78006. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2884647. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

