THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6, which is an IAA-glucose hydrolase, preferentially recognizes the structure of the indole ring
- PMID: 38514802
- PMCID: PMC10958001
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-57506-z
THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6, which is an IAA-glucose hydrolase, preferentially recognizes the structure of the indole ring
Abstract
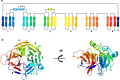
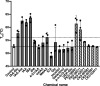
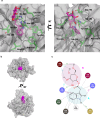
An indole-3-acetic acid (IAA)-glucose hydrolase, THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6 (TGW6), negatively regulates the grain weight in rice. TGW6 has been used as a target for breeding increased rice yield. Moreover, the activity of TGW6 has been thought to involve auxin homeostasis, yet the details of this putative TGW6 activity remain unclear. Here, we show the three-dimensional structure and substrate preference of TGW6 using X-ray crystallography, thermal shift assays and fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance (19F NMR). The crystal structure of TGW6 was determined at 2.6 Å resolution and exhibited a six-bladed β-propeller structure. Thermal shift assays revealed that TGW6 preferably interacted with indole compounds among the tested substrates, enzyme products and their analogs. Further analysis using 19F NMR with 1,134 fluorinated fragments emphasized the importance of indole fragments in recognition by TGW6. Finally, docking simulation analyses of the substrate and related fragments in the presence of TGW6 supported the interaction specificity for indole compounds. Herein, we describe the structure and substrate preference of TGW6 for interacting with indole fragments during substrate recognition. Uncovering the molecular details of TGW6 activity will stimulate the use of this enzyme for increasing crop yields and contributes to functional studies of IAA glycoconjugate hydrolases in auxin homeostasis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loss of function of the IAA-glucose hydrolase gene TGW6 enhances rice grain weight and increases yield.Nat Genet. 2013 Jun;45(6):707-11. doi: 10.1038/ng.2612. Epub 2013 Apr 14. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23583977
-
Source ability is regulated by THOUSAND-GRAIN WEIGHT 6 in rice.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025 May;222:109760. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109760. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40068459
-
Expression, purification and crystallization of TGW6, which limits grain weight in rice.Protein Expr Purif. 2021 Dec;188:105975. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2021.105975. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Protein Expr Purif. 2021. PMID: 34536500
-
Why plants need more than one type of auxin.Plant Sci. 2011 Mar;180(3):454-60. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.12.007. Epub 2010 Dec 22. Plant Sci. 2011. PMID: 21421392 Review.
-
Auxin conjugates: their role for plant development and in the evolution of land plants.J Exp Bot. 2011 Mar;62(6):1757-73. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq412. Epub 2011 Feb 9. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21307383 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic changes of endogenous phytohormones and carbohydrates during spontaneous morphogenesis of Centaurium erythraea Rafn.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Nov 6;15:1487897. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1487897. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39568459 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation pathways in auxin homeostasis.Physiol Plant. 2025 Mar-Apr;177(2):e70170. doi: 10.1111/ppl.70170. Physiol Plant. 2025. PMID: 40133767 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. World Food and Agriculture. FAO Statistical Yearbook 2021. 10.4060/cb4477en (2021).
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

