Disease staging of Alzheimer's disease using a CSF-based biomarker model
- PMID: 38514824
- PMCID: PMC11108782
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-024-00599-y
Disease staging of Alzheimer's disease using a CSF-based biomarker model
Abstract
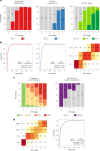
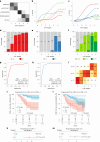
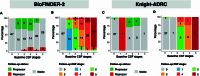
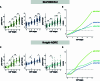
Biological staging of individuals with Alzheimer's disease (AD) may improve diagnostic and prognostic workup of dementia in clinical practice and the design of clinical trials. In this study, we used the Subtype and Stage Inference (SuStaIn) algorithm to establish a robust biological staging model for AD using cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers. Our analysis involved 426 participants from BioFINDER-2 and was validated in 222 participants from the Knight Alzheimer Disease Research Center cohort. SuStaIn identified a singular biomarker sequence and revealed that five CSF biomarkers effectively constituted a reliable staging model (ordered: Aβ42/40, pT217/T217, pT205/T205, MTBR-tau243 and non-phosphorylated mid-region tau). The CSF stages (0-5) demonstrated a correlation with increased abnormalities in other AD-related biomarkers, such as Aβ-PET and tau-PET, and aligned with longitudinal biomarker changes reflective of AD progression. Higher CSF stages at baseline were associated with an elevated hazard ratio of clinical decline. This study highlights a common molecular pathway underlying AD pathophysiology across all patients, suggesting that a single CSF collection can accurately indicate the presence of AD pathologies and characterize the stage of disease progression. The proposed staging model has implications for enhancing diagnostic and prognostic assessments in both clinical practice and the design of clinical trials.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
O.H. has acquired research support (for the institution) from ADx, AVID Radiopharmaceuticals, Biogen, Eli Lilly, Eisai, Fujirebio, GE Healthcare, Pfizer and Roche. In the past 2 years, he has received consultancy/speaker fees from AC Immune, Amylyx, Alzpath, BioArctic, Biogen, Cerveau, Eisai, Eli Lilly, Fujirebio, Genentech, Merck, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Roche, Sanofi and Siemens. J.W.V. is supported by the SciLifeLab & Wallenberg Data-Driven Life Science Program (grant: KAW 2020.0239). K.H. is an Eisai-sponsored voluntary research associate professor at Washington University and has received salary from Eisai. Washington University, R.J.B. and D.M.H. have equity ownership interest in C2N Diagnostics. R.J.B. and D.M.H. receive income from C2N Diagnostics for serving on the scientific advisory board. K.H., N.R.B. and R.J.B. may receive income based on technology (methods to detect MTBR tau isoforms and use thereof) licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. D.M.H. may receive income based on technology (antibodies to mid-domain of tau) licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. R.J.B. has received honoraria as a speaker, consultant or advisory board member from Amgen and Roche. D.M.H. is on the scientific advisory board of Genentech, Denali and Cajal Neurosciences and consults for Alector and Asteroid. N.R.B. is a co-inventor on the following US patent applications: ‘Methods to detect novel tau species in CSF and use thereof to track tau neuropathology in Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies’ (PCT/US2020/046224); ‘CSF phosphorylated tau and amyloid beta profiles as biomarkers of tauopathies’ (PCT/US2022/022906); and ‘Methods of diagnosing and treating based on site-specific tau phosphorylation’ (PCT/US2019/030725). N.R.B. may receive royalty income based on technology licensed by Washington University to C2N Diagnostics. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures











References
-
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Med.27, 954–963 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

