Roles of Histone Deacetylase 4 in the Inflammatory and Metabolic Processes
- PMID: 38514922
- PMCID: PMC11140402
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0174
Roles of Histone Deacetylase 4 in the Inflammatory and Metabolic Processes
Abstract
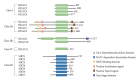
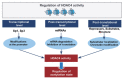
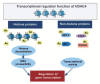
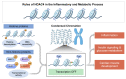
Histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4), a class IIa HDAC, has gained attention as a potential therapeutic target in treating inflammatory and metabolic processes based on its essential role in various biological pathways by deacetylating non-histone proteins, including transcription factors. The activity of HDAC4 is regulated at the transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational levels. The functions of HDAC4 are tissue-dependent in response to endogenous and exogenous factors and their substrates. In particular, the association of HDAC4 with non-histone targets, including transcription factors, such as myocyte enhancer factor 2, hypoxia-inducible factor, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, and forkhead box proteins, play a crucial role in regulating inflammatory and metabolic processes. This review summarizes the regulatory modes of HDAC4 activity and its functions in inflammation, insulin signaling and glucose metabolism, and cardiac muscle development.
Keywords: Histone deacetylases; Inflammation; Metabolism; Transcription factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Jenuwein T, Allis CD. Translating the histone code. Science. 2001;293:1074–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

