Systems approaches to scaling up: a systematic review and narrative synthesis of evidence for physical activity and other behavioural non-communicable disease risk factors
- PMID: 38515118
- PMCID: PMC10958859
- DOI: 10.1186/s12966-024-01579-6
Systems approaches to scaling up: a systematic review and narrative synthesis of evidence for physical activity and other behavioural non-communicable disease risk factors
Abstract
Background: Non-communicable diseases (NCDs) are the leading causes of death worldwide. Systems approaches have potential for creating sustainable outcomes at scale but have rarely been used to support scale up in physical activity/nutrition promotion or NCD prevention more generally. This review aimed to: (i) synthesise evidence on the use of systems approaches in scaling up interventions targeting four behavioural risk factors for NCDs; and (ii) to explore how systems approaches have been conceptualised and used in intervention implementation and scale up.
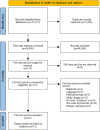
Method: Seven electronic databases were searched for studies published 2016-2021. Eligible studies targeted at least one of four NCD behavioural risk factors (physical inactivity, tobacco use, alcohol consumption, diet), or described evaluation of an intervention planned for or scaled up. Studies were categorised as having a (i) high, (ii) moderate, or (iii) no use of a systems approach. A narrative synthesis of how systems approaches had been operationalised in scale up, following PRISMA guidelines.
Results: Twenty-one intervention studies were included. Only 19% (n = 4) of interventions explicitly used systems thinking to inform intervention design, implementation and scale up (targeting all four risk factors n = 2, diet n = 1, tobacco use n = 1). Five studies ('high use') planned and implemented scale up with an explicit focus on relations between system elements and used system changes to drive impact at scale. Seven studies ('moderate use') considered systems elements impacting scale-up processes or outcomes but did not require achieving system-level changes from the outset. Nine studies ('no use') were designed to work at multiple levels among multiple agencies in an intervention setting, but the complexity of the system and relations between system elements was not articulated. We synthesised reported barriers and facilitators to scaling up, and how studies within each group conceptualised and used systems approaches, and methods, frameworks and principles for scaling up.
Conclusion: In physical activity research, and NCD prevention more broadly, the use of systems approaches in scale up remains in its infancy. For researchers, practitioners and policymakers wishing to adopt systems approaches to intervention implementation at scale, guidance is needed on how to communicate and operationalise systems approaches in research and in practice.
Trial registration: PROSPERO (CRD42021287265).
Keywords: Alcohol; Diet; Implementation; Non-communicable diseases; Nutrition; Public health; Scale up; System; Tobacco.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Strategies for enhancing the implementation of school-based policies or practices targeting diet, physical activity, obesity, tobacco or alcohol use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Dec 12;12(12):CD011677. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011677.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39665378
-
Targeted mass media interventions promoting healthy behaviours to reduce risk of non-communicable diseases in adult, ethnic minorities.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 17;2(2):CD011683. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011683.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28211056 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for enhancing the implementation of school-based policies or practices targeting risk factors for chronic disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 29;11(11):CD011677. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011677.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 29;8:CD011677. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011677.pub3. PMID: 29185627 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Nutritional interventions for survivors of childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Aug 22;2016(8):CD009678. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009678.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27545902 Free PMC article.
-
Tobacco packaging design for reducing tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 27;4(4):CD011244. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011244.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28447363 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Process evaluation of a participatory systems approach to promote health and well-being among students at vocational schools.Health Educ Res. 2025 May 31;40(3):cyaf022. doi: 10.1093/her/cyaf022. Health Educ Res. 2025. PMID: 40448680 Free PMC article.
-
University-based physical education as a structured temporal and spatial opportunity for shaping health-oriented lifestyles.Front Public Health. 2025 May 21;13:1597480. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1597480. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40469591 Free PMC article.
-
Applying a participatory system dynamics approach to childhood overweight and obesity in the local context: reflections from the LIKE project.Health Res Policy Syst. 2025 May 26;23(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12961-025-01345-5. Health Res Policy Syst. 2025. PMID: 40420221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Collaborative Network, Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 (GBD 2019) Results (2020, Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation – IHME) https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results/. 2019.
-
- World Health Organization . Global action plan for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases 2013–2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Action Plan on Physical Activity 2018–2030: more active people for a healthier world. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018.
-
- World Health Organization . Global Alcohol Action Plan 2022–2030. Geneva: Switzerland; 2022.
-
- World Health Organization . Global status report on physical activity 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical