Advances in research on the anti-tumor mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides
- PMID: 38515577
- PMCID: PMC10955345
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1334915
Advances in research on the anti-tumor mechanism of Astragalus polysaccharides
Abstract
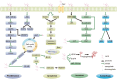
The dry root of the soybean plant Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch) Bge. var. mongholicus (Bge) Hsiao or A. membranaceus (Fisch) Bge, Astragali Radix (AR) has a long medicinal history. Astragalus polysaccharide (APS), the natural macromolecule that exhibits immune regulatory, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, and other pharmacological activities, is an important active ingredient extracted from AR. Recently, APS has been increasingly used in cancer therapy owing to its anti-tumor ability as it prevents the progression of prostate, liver, cervical, ovarian, and non-small-cell lung cancer by suppressing tumor cell growth and invasion and enhancing apoptosis. In addition, APS enhances the sensitivity of tumors to antineoplastic agents and improves the body's immunity. This macromolecule has prospects for broad application in tumor therapy through various pathways. In this article, we present the latest progress in the research on the anti-tumor effects of APS and its underlying mechanisms, aiming to provide novel theoretical support and reference for its use in cancer therapy.
Keywords: Astragalus polysaccharides; anti-tumor mechanism; anti-tumor therapy; apoptosis; autophagy; cancer.
Copyright © 2024 Yang, Meng, Zhang and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fitzmaurice C, Allen C, Barber RM, Barregard L, Bhutta ZA, Brenner H, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 cancer groups, 1990 to 2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. (2017) 3:524–48. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

