Evolution of dosimetric treatment planning for pediatric total lymphoid irradiation (TLI): a single-institution experience
- PMID: 38515822
- PMCID: PMC10954272
- DOI: 10.5603/rpor.98734
Evolution of dosimetric treatment planning for pediatric total lymphoid irradiation (TLI): a single-institution experience
Abstract
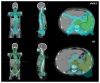
Background: Total lymphoid irradiation (TLI) is a conditioning regimen in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (allo-HSCT) which may reduce long-term toxicities attributed to other techniques, such as total body irradiation (TBI). At our institution, TLI treatments were first planned with the three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy (3D-CRT) technique and later with volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT). With the recent availability of a basic helical tomotherapy (HT), the possible dosimetric gain of the latter for TLI is studied.
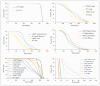
Materials and methods: 22 pediatric patients were planned for VMAT and HT, prescribed to 8 Gy in 4 fractions. VMAT was planned with template based on a single cost function, using the Monaco treatment planning system (TPS). HT plans were planned using Accuray Precision TPS for a basic HT without the dynamic jaws feature or VOLO-Ultra algorithm. Plan quality was analyzed based on four quality indices, mean and maximum doses to planning target volume (PTV) and organs at risk (OARs), dose gradient and integral doses. Differences were analyzed with Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results: HT plans resulted in improved conformity (CI) and homogeneity indices (HI) (p < 0.05) but less steep dose gradient (p = 0.181). VMAT plans created larger areas with high doses within the PTV, while comparable doses to OARs, except mainly for the spinal marrow, for which a reduction of 37.7% in D2% was obtained (p < 0.05). Integral dose for non-tumor tissue was 11.3% lower with the VMAT template (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: HT achieves better conformity and homogeneity even without its more advanced features. Nevertheless, the VMAT template achieves dosimetric results close to those of HT, both with similar clinical outcome.
Keywords: VMAT; tomotherapy; total lymphoid irradiation.
© 2023 Greater Poland Cancer Centre.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Saglio F, Zecca M, Pagliara D, et al. Occurrence of long-term effects after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children affected by acute leukemia receiving either busulfan or total body irradiation: results of an AIEOP (Associazione Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica) retrospective study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(10):1918–1927. doi: 10.1038/s41409-020-0806-8. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
