Effect of 24-form simplified Tai Chi on executive inhibitory control of college students: a randomized controlled trial of EEG
- PMID: 38515964
- PMCID: PMC10955120
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1344989
Effect of 24-form simplified Tai Chi on executive inhibitory control of college students: a randomized controlled trial of EEG
Abstract
Background: College students, undergoing crucial cognitive development, face challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic that impact their executive functions. While existing research indicates positive effects of Tai Chi (TC) on college students' cognitive abilities, there is a scarcity of studies investigating its impact on executive functions and frontal brain activity.
Objective: This study aimed to compare the effects of 24-form simplified TC training on college students' executive functions and frontal brain electrical activity. The hypothesis posited that the TC group would exhibit superior performance compared to the control group during COVID-19 pandemic.
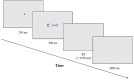
Method: Seventy college students were randomly assigned to either TC group or control group, engaging in 36 sessions (3 sessions per week, 45 min each) over 12 weeks. Executive inhibitory control was assessed using the Stroop Color and Word Test, and resting brain electrical activity in the frontal area was recorded through Electroencephalography.
Result: ACC was influenced by group, group-time interaction, and Stroop task-time interaction. RT was affected by time, task condition, task condition-time interaction, and task condition-group interaction. Notably, the TC group showed improved ACC (from 96.54 ± 3.27% to 98.90 ± 1.32%) and decreased RT (from 0.73 ± 0.12 to 0.66 ± 0.07 s), particularly in the inconsistent task. Regarding EEG band power, significant Group and Time interaction effects were found in F3-θ, F3-α, F3-β, F4-θ, and F4-α. Moreover, within the TC group, significant increases in F3-θ band power (from 4.66 ± 3.55 to 7.71 ± 8.44) and F4-θ band power (from 4.41 ± 2.82 to 8.61 ± 9.51) (10-3·μV·Hz) were noted pre-and post-tests. In the control group, significant decreases were observed in F3-α band power (from 5.18 ± 4.61 to 2.79 ± 2.11) and F4-α band power (from 5.57 ± 6.58 to 2.48 ± 1.95) (10-3·μV·Hz).
Conclusion: The pandemic-induced panic may impact frontal lobe brain activity in college students. TC training not only improves executive inhibitory control but may also enhance localized brain activity, suggesting its potential as a holistic intervention for cognitive and neurological well-being during stressful periods.
Keywords: accuracy; inconsistent task; reaction time; α band power; β band power; θ band power.
Copyright © 2024 Wang and Lyu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
-
- Celia G., Cavicchiolo E., Girelli L., Limone P., Cozzolino M. (2022). Effect of online counselling on emotional outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic: an innovative group intervention for university students using the brain wave modulation technique. Couns. Psychother. Res. 22, 889–901. doi: 10.1002/capr.12512, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clay J. M., Stafford L. D., Parker M. O. (2023). Associations between self-reported inhibitory control, stress, and alcohol (mis) use during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK: a national cross-sectional study utilising data from four birth cohorts. Int. J. Ment. Heal. Addict. 21, 350–371. doi: 10.1007/s11469-021-00599-8, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Douris P. C., Cottone J., Cruz P., Frosos N., Marino C., Singamenggala L., et al. . (2022). The effects of externally paced exercise on executive function and stress in college-aged students. J. Sci. Sport Exerc. 5, 149–155. doi: 10.1007/s42978-022-00173-1 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous