The efflux pumps Rv1877 and Rv0191 play differential roles in the protection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis against chemical stress
- PMID: 38516013
- PMCID: PMC10956863
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1359188
The efflux pumps Rv1877 and Rv0191 play differential roles in the protection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis against chemical stress
Abstract
Background: It was previously shown that GlnA3sc enabled Streptomyces coelicolor to survive in excess polyamines. However, subsequent studies revealed that Rv1878, the corresponding Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) ortholog, was not essential for the detoxification of spermine (Spm), in M.tb. On the other hand, the multi-drug efflux pump Rv1877 was previously shown to enable export of a wide range of compounds, while Rv0191 was shown to be more specific to chloramphenicol.
Rationale: Therefore, we first wanted to determine if detoxification of Spm by efflux can be achieved by any efflux pump, or if that was dependent upon the function of the pump. Next, since Rv1878 was found not to be essential for the detoxification of Spm, we sought to follow-up on the investigation of the physiological role of Rv1878 along with Rv1877 and Rv0191.
Approach: To evaluate the specificity of efflux pumps in the mycobacterial tolerance to Spm, we generated unmarked ∆rv1877 and ∆rv0191 M.tb mutants and evaluated their susceptibility to Spm. To follow up on the investigation of any other physiological roles they may have, we characterized them along with the ∆rv1878 M.tb mutant.
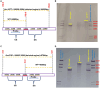
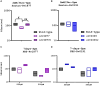
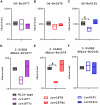
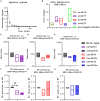
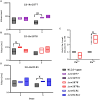
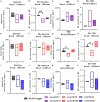
Results: The ∆rv1877 mutant was sensitive to Spm stress, while the ∆rv0191 mutant was not. On the other hand, the ∆rv1878 mutant grew better than the wild-type during iron starvation yet was sensitive to cell wall stress. The proteins Rv1877 and Rv1878 seemed to play physiological roles during hypoxia and acidic stress. Lastly, the ∆rv0191 mutant was the only mutant that was sensitive to oxidative stress.
Conclusion: The multidrug MFS-type efflux pump Rv1877 is required for Spm detoxification, as opposed to Rv0191 which seems to play a more specific role. Moreover, Rv1878 seems to play a role in the regulation of iron homeostasis and the reconstitution of the cell wall of M.tb. On the other hand, the sensitivity of the ∆rv0191 mutant to oxidative stress, suggests that Rv0191 may be responsible for the transport of low molecular weight thiols.
Keywords: MFS-type pump; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Rv0191; Rv1877; Rv1878; cell wall stress; iron homeostasis; spermine stress.
Copyright © 2024 Sao Emani and Reiling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv0191 is an efflux pump of major facilitator superfamily transporter regulated by Rv1353c.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019 May 30;667:59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2019.04.010. Epub 2019 May 1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2019. PMID: 31054279
-
GlnA3Mt is able to glutamylate spermine but it is not essential for the detoxification of spermine in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Bacteriol. 2025 Feb 20;207(2):e0043924. doi: 10.1128/jb.00439-24. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Bacteriol. 2025. PMID: 39882905 Free PMC article.
-
The Putative Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) Protein Named Rv1877 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Behaves as a Multidrug Efflux Pump.Curr Microbiol. 2022 Sep 20;79(11):324. doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-03021-1. Curr Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36125560
-
Efflux pump inhibitors as a promising adjunct therapy against drug resistant tuberculosis: a new strategy to revisit mycobacterial targets and repurpose old drugs.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020 Aug;18(8):741-757. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1760845. Epub 2020 May 20. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2020. PMID: 32434397 Review.
-
In Silico Approach for Phytocompound-Based Drug Designing to Fight Efflux Pump-Mediated Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021 Jun;193(6):1757-1779. doi: 10.1007/s12010-021-03557-1. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33826064 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating genomic, transcriptomic, and phenotypic information to explore drug resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis sub-lineage 4.2.2.2.J Appl Microbiol. 2025 Mar 3;136(3):lxaf063. doi: 10.1093/jambio/lxaf063. J Appl Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40074543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams L. B., Dinauer M. C., Morgenstern D. E., Krahenbuhl J. L. (1997). Comparison of the roles of reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in the host response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis using transgenic mice. Tuber. Lung Dis. 78, 237–246. doi: 10.1016/S0962-8479(97)90004-6, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahidjo B. A., Kuhnert D., McKenzie J. L., Machowski E. E., Gordhan B. G., Arcus V., et al. . (2011). VapC toxins from Mycobacterium tuberculosis are ribonucleases that differentially inhibit growth and are neutralized by cognate VapB antitoxins. PLoS One 6:e21738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021738, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

