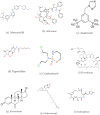
Molecular structural modeling and physical characteristics of anti-breast cancer drugs via some novel topological descriptors and regression models
- PMID: 38516623
- PMCID: PMC10955308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crstbi.2024.100134
Molecular structural modeling and physical characteristics of anti-breast cancer drugs via some novel topological descriptors and regression models
Abstract
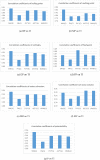
Research is continuously being pursued to treat cancer patients and prevent the disease by developing new medicines. However, experimental drug design and development is a costly, time-consuming, and challenging process. Alternatively, computational and mathematical techniques play an important role in optimally achieving this goal. Among these mathematical techniques, topological indices (TIs) have many applications in the drugs used for the treatment of breast cancer. TIs can be utilized to forecast the effectiveness of drugs by providing molecular structure information and related properties of the drugs. In addition, these can assist in the design and discovery of new drugs by providing insights into the structure-property/structure-activity relationships. In this article, a Quantitative Structure Property Relationship (QSPR) analysis is carried out using some novel degree-based molecular descriptors and regression models to predict various properties (such as boiling point, melting point, enthalpy, flashpoint, molar refraction, molar volume, and polarizability) of 14 drugs used for the breast cancer treatment. The molecular structures of these drugs are topologically modeled through vertex and edge partitioning techniques of graph theory, and then linear regression models are developed to correlate the computed values with the experimental properties of the drugs to investigate the performance of TIs in predicting these properties. The results confirmed the potential of the considered topological indices as a tool for drug discovery and design in the field of breast cancer treatment.
Keywords: Drugs; Graph theory; Molecular structure; QSPR analysis; Topological indices.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Arockiaraj M., Paul D., Clement J., Tigga S., Jacob K., Balasubramanian K. Novel molecular hybrid geometric-harmonic-Zagreb degree based descriptors and their efficacy in QSPR studies of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2023;34(7):569–589. doi: 10.1080/1062936X.2023.2239149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aslam A., Ahmad S., Gao W. On certain topological indices of boron triangular nanotubes. Z. Naturforsch. 2017;72(8):711–716.
-
- Aslam A., Bashir Y., Ahmad S., Gao W. On topological indices of certain dendrimer structures. Z. Naturforsch. 2017;72(6):559–566.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources