Peptide and Protein Desulfurization with Diboron Reagents
- PMID: 38517348
- PMCID: PMC10999128
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.4c00609
Peptide and Protein Desulfurization with Diboron Reagents
Abstract
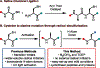
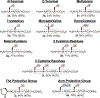
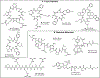
In this Letter, we report a direct and robust desulfurization method employing water-soluble phosphine, specifically tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydrochloride (TCEP), and tetrahydroxydiboron (B2(OH)4), which serves as a radical initiator. This innovative reaction exhibits compatibility with a diverse array of substrates, including cysteine residues in chemically synthesized oligopeptides and cyclic peptides, alkyl thiols in bioactive molecules, disulfides in commercial proteins, and selenocysteine. We optimized the reaction conditions to minimize the formation of undesired oxidized and borylated byproducts. Furthermore, the refined desulfurization process is executed after native chemical ligation (NCL) in a single pot, streamlining the existing synthetic approaches. This demonstrates its potential applications in the synthesis of complex peptides and proteins, showcasing a significant advancement in the field.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kent SBH Total chemical synthesis of proteins. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 338–351. - PubMed
-
- Total Chemical Synthesis of Proteins; Brik A.; Dawson P.; Liu L., Eds.; Wiley, 2021.
-
- Kulkarni SS; Sayers J; Premdjee B; Payne RJ Rapid and efficient protein synthesis through expansion of the native chemical ligation concept. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 0122.
-
- Dawson PE; Muir TW; Clark-Lewis I; Kent SBH Synthesis of Proteins by Native Chemical Ligation. Science 1994, 266, 776–779. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

