Quorum quenching effect of cyclodextrins on the pyocyanin and pyoverdine production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 38517512
- PMCID: PMC10959793
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-024-13104-7
Quorum quenching effect of cyclodextrins on the pyocyanin and pyoverdine production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
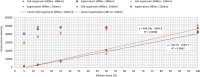
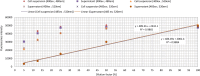
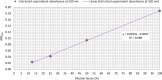
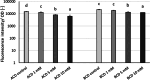
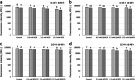
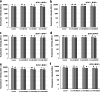
Various virulence determinants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa are regulated by the quorum sensing (QS) network producing and releasing signalling molecules. Two of these virulence determinants are the pyocyanin and pyoverdine, which interfere with multiple cellular functions during infection. The application of QS-inhibiting agents, such as cyclodextrins (CDs), appears to be a promising approach. Further to method development, this research tested in large-volume test systems the effect of α- and β-CD (ACD, BCD) at 1, 5, and 10 mM concentrations on the production of pyocyanin in the P. aeruginosa model system. The concentration and time-dependent quorum quenching effect of native CDs and their derivatives on pyoverdine production was tested in a small-volume high-throughput system. In the large-volume system, both ACD and BCD significantly inhibited pyocyanin production, but ACD to a greater extent. 10 mM ACD resulted in 58% inhibition, while BCD only ~40%. Similarly, ACD was more effective in the inhibition of pyoverdine production; nevertheless, the results of RMANOVA demonstrated the significant efficiency of both ACD and BCD, as well as their derivatives. Both the contact time and the cyclodextrin treatments significantly influenced pyoverdine production. In this case, the inhibitory effect of ACD after 48 h at 12.5 mM was 57%, while the inhibitory effect of BCD and its derivatives was lower than 40%. The high-level significant inhibition of both pyocyanin and pyoverdine production by ACD was detectable. Consequently, the potential value of CDs as QS inhibitors and the antivirulence strategy should be considered. KEYPOINTS: • Applicability of a simplified method for quantification of pyocyanin production was demonstrated. • The cyclodextrins significantly affected the pyocyanin and pyoverdine production. • The native ACD exhibited the highest attenuation in pyoverdine production.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; Cyclodextrins; Pyocyanin; Pyoverdine; Quorum quenching; Quorum sensing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgR Phosphorylation Status Differentially Regulates Pyocyanin and Pyoverdine Production.mBio. 2018 Jan 30;9(1):e02318-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02318-17. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29382736 Free PMC article.
-
Bactericidal effect of Iberin combined with photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm cultured on ex vivo wound model.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023 Dec;44:103841. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2023.103841. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023. PMID: 37832710
-
Pathogenesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Biofilm-Associated Is Dependent on the Pyoverdine and Pyocyanin Siderophores by Quorum Sensing Modulation.Microb Ecol. 2023 Jul;86(1):727-741. doi: 10.1007/s00248-022-02095-5. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Microb Ecol. 2023. PMID: 35948833
-
A biomedical perspective of pyocyanin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: its applications and challenges.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 10;40(3):90. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-03889-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38341389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesamin and sesamolin rescues Caenorhabditis elegans from Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection through the attenuation of quorum sensing regulated virulence factors.Microb Pathog. 2021 Jun;155:104912. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.104912. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Microb Pathog. 2021. PMID: 33932548 Review.
Cited by
-
Pigments from pathogenic bacteria: a comprehensive update on recent advances.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 20;40(9):270. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-04076-x. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39030429 Review.
-
FTY720 Reduces the Biomass of Biofilms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a Dose-Dependent Manner.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 4;13(7):621. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070621. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061303 Free PMC article.
-
Green Biosynthesis of Bimetallic Copper Oxide-Selenium Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extract of Lagenaria Siceraria: Antibacterial, Anti-Virulence Activities Against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Apr 14;20:4705-4727. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S497494. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40255676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas HA, Shaldam MA, Eldamasi D (2020) Curtailing quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Sitagliptin. Curr Microbiol 77:1051–1060. 10.1007/s00284-020-01909-4 - PubMed
-
- Ahmad A, Viljoen AM, Chenia HY (2015) The impact of plant volatiles on bacterial quorum sensing. Let Appl Microbiol 60:8–19. 10.1111/lam.12343 - PubMed
-
- Albesa I, Barberis LI, Pájaro MC, Eraso AJ (1985) Pyoverdine production by Pseudomonas fluorescens in synthetic media with various sources of nitrogen. J Gen Microbiol 131:3251–3254. 10.1099/00221287-131-12-3251
-
- Azam MW, Khan AU (2019) Updates on the pathogenicity status of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Drug Discov 24:350–359. 10.1016/j.drudis.2018.07.003 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

