Hemodynamic management of cardiogenic shock in the intensive care unit
- PMID: 38518863
- PMCID: PMC11148863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.healun.2024.03.009
Hemodynamic management of cardiogenic shock in the intensive care unit
Abstract
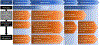
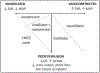
Hemodynamic derangements are defining features of cardiogenic shock. Randomized clinical trials have examined the efficacy of various therapeutic interventions, from percutaneous coronary intervention to inotropes and mechanical circulatory support (MCS). However, hemodynamic management in cardiogenic shock has not been well-studied. This State-of-the-Art review will provide a framework for hemodynamic management in cardiogenic shock, including a description of the 4 therapeutic phases from initial 'Rescue' to 'Optimization', 'Stabilization' and 'de-Escalation or Exit therapy' (R-O-S-E), phenotyping and phenotype-guided tailoring of pharmacological and MCS support, to achieve hemodynamic and therapeutic goals. Finally, the premises that form the basis for clinical management and the hypotheses for randomized controlled trials will be discussed, with a view to the future direction of cardiogenic shock.
Keywords: cardiogenic shock; heart transplantation; hemodynamics; inotropes; left ventricular assist devices; mechanical circulatory support.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest SL has received honoraria from Abiomed. JGC reports having received fees for educational presentations from Abbott and Orion and consultancies and travel grants from Abbott. JB has received honoraria from Abiomed, Getinge, Resuscitec and Xenios. EZ reports no relevant conflict of interest with respect to the content of this manuscript. VB has reported no conflict of interest. BS has received research support from the German Research Foundation, the Else Kröner-Fresenius-Stiftung and Abiomed as well as speaker fees from Abbott, Abiomed and AstraZeneca, outside of the submitted work. TH has received a research grant through the ISHLT funded by Abiomed.
Figures




References
-
- Jeger RV, Assmann SF, Yehudai L, et al. Causes of death and re-hospitalization in cardiogenic shock. Acute Card Care 2007;9:25–33. - PubMed
-
- Abraham J, Blumer V, Burkhoff D, et al. Heart failure-related cardiogenic shock: pathophysiology, evaluation and management considerations: review of heart failure-related cardiogenic shock. J Card Fail 2021;27:1126–40. - PubMed
-
- Lim HS, Howell N. Cardiogenic shock due to end-stage heart failure and acute myocardial infarction: characteristics and outcome of temporary mechanical circulatory support. Shock 2018;50:167–72. - PubMed

