Molecular basis promoting centriole triplet microtubule assembly
- PMID: 38519454
- PMCID: PMC10960023
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-46454-x
Molecular basis promoting centriole triplet microtubule assembly
Abstract
The triplet microtubule, a core structure of centrioles crucial for the organization of centrosomes, cilia, and flagella, consists of unclosed incomplete microtubules. The mechanisms of its assembly represent a fundamental open question in biology. Here, we discover that the ciliopathy protein HYLS1 and the β-tubulin isotype TUBB promote centriole triplet microtubule assembly. HYLS1 or a C-terminal tail truncated version of TUBB generates tubulin-based superstructures composed of centriole-like incomplete microtubule chains when overexpressed in human cells. AlphaFold-based structural models and mutagenesis analyses further suggest that the ciliopathy-related residue D211 of HYLS1 physically traps the wobbling C-terminal tail of TUBB, thereby suppressing its inhibitory role in the initiation of the incomplete microtubule assembly. Overall, our findings provide molecular insights into the biogenesis of atypical microtubule architectures conserved for over a billion years.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


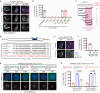
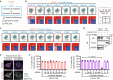
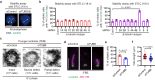
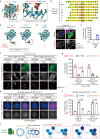
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 19H05651/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 21J21492/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 23H02627/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 22K19305/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 23H00394/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 20K22701/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 21H02623/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- 22K19370/MEXT | Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS)
- JPMJCR22E1/MEXT | Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)
- JPMJPR21EC/MEXT | Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

