TCMNPAS: a comprehensive analysis platform integrating network formulaology and network pharmacology for exploring traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 38519956
- PMCID: PMC10958928
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00924-y
TCMNPAS: a comprehensive analysis platform integrating network formulaology and network pharmacology for exploring traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
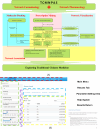
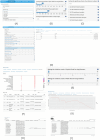
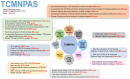
The application of network formulaology and network pharmacology has significantly advanced the scientific understanding of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) treatment mechanisms in disease. The field of herbal biology is experiencing a surge in data generation. However, researchers are encountering challenges due to the fragmented nature of the data and the reliance on programming tools for data analysis. We have developed TCMNPAS, a comprehensive analysis platform that integrates network formularology and network pharmacology. This platform is designed to investigate in-depth the compatibility characteristics of TCM formulas and their potential molecular mechanisms. TCMNPAS incorporates multiple resources and offers a range of functions designed for automated analysis implementation, including prescription mining, molecular docking, network pharmacology analysis, and visualization. These functions enable researchers to analyze and obtain core herbs and core formulas from herbal prescription data through prescription mining. Additionally, TCMNPAS facilitates virtual screening of active compounds in TCM and its formulas through batch molecular docking, allowing for the rapid construction and analysis of networks associated with "herb-compound-target-pathway" and disease targets. Built upon the integrated analysis concept of network formulaology and network pharmacology, TCMNPAS enables quick point-and-click completion of network-based association analysis, spanning from core formula mining from clinical data to the exploration of therapeutic targets for disease treatment. TCMNPAS serves as a powerful platform for uncovering the combinatorial rules and mechanism of TCM formulas holistically. We distribute TCMNPAS within an open-source R package at GitHub ( https://github.com/yangpluszhu/tcmnpas ), and the project is freely available at http://54.223.75.62:3838/ .
Keywords: Core formula mining; Molecular docking; Molecular mechanism; Network pharmacology analysis system; TCMNPAS; Traditional Chinese medicine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
There is no competing interests involved in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Fan XH, Cheng YY, Zhang BL. Network formulaology: a new strategy for modern research of traditional Chinese medicine formulae. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015;40(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Fan XH, Xiao S, Ai N, Liao J, Cheng YY. Dissecting functional chemome of Xiaoqinglong decoction analogous formulae using network formulaology approach. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015;40(13):2634–2638. - PubMed
-
- Wang X, Wang ZY, Zheng JH, Li S. TCM network pharmacology: a new trend towards combining computational, experimental and clinical approaches. Chin J Nat Med. 2021;19(1):1–11. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 22ZR1462100/Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai
- 22YF1440300/Shanghai sailing program
- YG2022QN015/Shanghai Jiaotong University "Jiaotong University Star" program
- SHDC2022CRW006/Demonstration-oriented Research Ward Construction Project of Shanghai Hospital Development Center
- 21S21902300/Medical science and technology support project of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission
- A1-U21-205-902/Shanghai Municipal Education Commission Collaborative Innovation Center, Clinical Evaluation Platform for Traditional Chinese Medicine and Chinese Patent Medicine
- SHDC2023CRS026/Special training program of Shanghai Hospital Development Center
- 23KFL077/Science and Technology Development Project of Shanghai University of traditional Chinese Medicine
- ZYZK007-005/Evidence based capacity building project of basic traditional Chinese Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

