Recent advances in the potential effects of natural products from traditional Chinese medicine against respiratory diseases targeting ferroptosis
- PMID: 38519984
- PMCID: PMC10958864
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-024-00918-w
Recent advances in the potential effects of natural products from traditional Chinese medicine against respiratory diseases targeting ferroptosis
Abstract
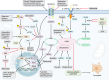
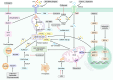
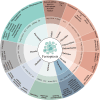
Respiratory diseases, marked by structural changes in the airways and lung tissues, can lead to reduced respiratory function and, in severe cases, respiratory failure. The side effects of current treatments, such as hormone therapy, drugs, and radiotherapy, highlight the need for new therapeutic strategies. Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) offers a promising alternative, leveraging its ability to target multiple pathways and mechanisms. Active compounds from Chinese herbs and other natural sources exhibit anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antitumor, and immunomodulatory effects, making them valuable in preventing and treating respiratory conditions. Ferroptosis, a unique form of programmed cell death (PCD) distinct from apoptosis, necrosis, and others, has emerged as a key area of interest. However, comprehensive reviews on how natural products influence ferroptosis in respiratory diseases are lacking. This review will explore the therapeutic potential and mechanisms of natural products from TCM in modulating ferroptosis for respiratory diseases like acute lung injury (ALI), asthma, pulmonary fibrosis (PF), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), lung ischemia-reperfusion injury (LIRI), pulmonary hypertension (PH), and lung cancer, aiming to provide new insights for research and clinical application in TCM for respiratory health.
Keywords: Ferroptosis; Mechanism; Natural products; Respiratory diseases; TCM.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

