ACR benchmark testing of a novel high-speed ring-gantry linac kV-CBCT system
- PMID: 38520072
- PMCID: PMC11087172
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.14299
ACR benchmark testing of a novel high-speed ring-gantry linac kV-CBCT system
Abstract
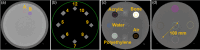
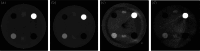
A new generation cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) system with new hardware design and advanced image reconstruction algorithms is available for radiation treatment simulation or adaptive radiotherapy (HyperSight CBCT imaging solution, Varian Medical Systems-a Siemens Healthineers company). This study assesses the CBCT image quality metrics using the criteria routinely used for diagnostic CT scanner accreditation as a first step towards the future use of HyperSight CBCT images for treatment planning and target/organ delineations. Image performance was evaluated using American College of Radiology (ACR) Program accreditation phantom tests for diagnostic computed tomography systems (CTs) and compared HyperSight images with a standard treatment planning diagnostic CT scanner (Siemens SOMATOM Edge) and with existing CBCT systems (Varian TrueBeam version 2.7 and Varian Halcyon version 2.0). Image quality performance for all Varian HyperSight CBCT vendor-provided imaging protocols were assessed using ACR head and body ring CT phantoms, then compared to existing imaging modalities. Image quality analysis metrics included contrast-to-noise (CNR), spatial resolution, Hounsfield number (HU) accuracy, image scaling, and uniformity. All image quality assessments were made following the recommendations and passing criteria provided by the ACR. The Varian HyperSight CBCT imaging system demonstrated excellent image quality, with the majority of vendor-provided imaging protocols capable of passing all ACR CT accreditation standards. Nearly all (8/11) vendor-provided protocols passed ACR criteria using the ACR head phantom, with the Abdomen Large, Pelvis Large, and H&N vendor-provided protocols produced HU uniformity values slightly exceeding passing criteria but remained within the allowable minor deviation levels (5-7 HU maximum differences). Compared to other existing CT and CBCT imaging modalities, both HyperSight Head and Pelvis imaging protocols matched the performance of the SOMATOM CT scanner, and both the HyperSight and SOMATOM CT substantially surpassed the performance of the Halcyon 2.0 and TrueBeam version 2.7 systems. Varian HyperSight CBCT imaging system could pass almost all tests for all vendor-provided protocols using ACR accreditation criteria, with image quality similar to those produced by diagnostic CT scanners and significantly better than existing linac-based CBCT imaging systems.
Keywords: ACR; CBCT; treatment planning.
© 2024 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics is published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was, in part, financially sponsored by Varian Medical Systems. Investigators independently designed and performed the study.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Image quality characterization of an ultra-high-speed kilovoltage cone-beam computed tomography imaging system on an O-ring linear accelerator.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 May;25(5):e14337. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14337. Epub 2024 Apr 4. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 38576183 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of a prototype rapid kilovoltage x-ray image guidance system designed for a ring shape radiation therapy unit.Med Phys. 2019 Mar;46(3):1355-1370. doi: 10.1002/mp.13396. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30675902 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of HyperSight CBCT for adaptive radiation therapy: A phantom benchmark study of dose calculation accuracy and delivery verification on the Halcyon.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Sep;26(9):e70245. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70245. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40926273 Free PMC article.
-
AAPM Task Group Report 238: 3D C-arms with volumetric imaging capability.Med Phys. 2023 Aug;50(8):e904-e945. doi: 10.1002/mp.16245. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36710257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review of consensus test methods in medical imaging and current practices in photoacoustic image quality assessment.J Biomed Opt. 2021 Sep;26(9):090901. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.26.9.090901. J Biomed Opt. 2021. PMID: 34510850 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-institutional study on image quality for a novel CBCT solution on O-ring linac.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Jun;26(6):e70023. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70023. Epub 2025 Mar 6. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40048322 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of knowledge-based planning models for male pelvic CBCT-based online adaptive radiotherapy on conventional linear accelerators.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024 Sep;25(9):e14464. doi: 10.1002/acm2.14464. Epub 2024 Jul 19. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2024. PMID: 39031902 Free PMC article.
-
Implementation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography-Guided Online Adaptive Radiotherapy for Challenging Trimodal Therapy in Bladder Preservation: A Report of Two Cases.Cureus. 2024 Aug 16;16(8):e66993. doi: 10.7759/cureus.66993. eCollection 2024 Aug. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39280408 Free PMC article.
-
Localization accuracy of 6-second CBCT for lung IGRT with various breathing patterns.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025 Jul;26(7):e70130. doi: 10.1002/acm2.70130. Epub 2025 May 29. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2025. PMID: 40439857 Free PMC article.
-
Dose calculation accuracy of clinical radiotherapy plans using next generation cone beam computed tomography imaging technology.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025 Mar 22;34:100756. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2025.100756. eCollection 2025 Apr. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40213030 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bushberg JT, Seibert AJ, Leidholdt Jr EM, Boone JM. The Essential Physics of Medical Imaging. 4th ed. Wolters Kluwer; 2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

