Postoperative chemotherapy relative dose intensity and overall survival in patients with colon cancer
- PMID: 38520557
- PMCID: PMC11417131
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-024-04665-5
Postoperative chemotherapy relative dose intensity and overall survival in patients with colon cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Quantifying the association of chemotherapy relative dose intensity (RDI) with overall survival may enable supportive care interventions that improve chemotherapy RDI to estimate their magnitude of potential clinical benefit.
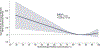
Methods: This cohort study included 533 patients with stage II-III colon cancer who initiated a planned regimen of 12 cycles of 5-fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX) chemotherapy. The primary exposure was chemotherapy RDI. The primary outcome was overall survival. Restricted cubic splines estimated hazard ratios (HR).
Results: Chemotherapy regimen RDI was associated with overall survival in an L-shaped pattern (linear P = 0.006; nonlinear P = 0.057); the risk of death was flat above 85% but increased linearly below 85%. For example, a decrease in RDI from 85 to 75% was associated with an increased risk of death [HR: 1.20 (95% CI: 1.08, 1.52)], whereas an increase in RDI from 85 to 95% was not associated with the risk of death [HR: 1.06 (95% CI: 0.82, 1.38)].
Conclusion: If chemotherapy RDI is considered a potential surrogate of overall survival, supportive care interventions that improve chemotherapy RDI might confer a potential clinical benefit in this population.
Keywords: Adherence; Chemotherapy; Surrogate endpoint; Toxicity.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
Dr. Brown reports receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute, Cancer Research UK, and the American Institute for Cancer Research during the study. Dr. Meyerhardt reports receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute during the study and consulting fees from Merck Pharmaceutical during the 36 months before publication (all fees <$5,000). Dr. Caan reports receiving grants from the National Cancer Institute during the study. All other authors report no disclosures.
Figures
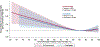
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage III colon cancer: relative dose intensity and survival among veterans.BMC Cancer. 2015 Feb 18;15:62. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1038-y. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25884851 Free PMC article.
-
Survival Impact of CAPOX Versus FOLFOX in the Adjuvant Treatment of Stage III Colon Cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018 Jun;17(2):156-163. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Feb 7. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29486916
-
Effect of Adjuvant FOLFOX Chemotherapy Duration on Outcomes of Patients With Stage III Colon Cancer.Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2015 Dec;14(4):262-8.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.clcc.2015.05.010. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26123496
-
[Progression of adjuvant chemotherapy for colon cancer].Ai Zheng. 2005 Dec;24(12):1546-9. Ai Zheng. 2005. PMID: 16351811 Review. Chinese.
-
Association Between Adjuvant Chemotherapy Duration and Survival Among Patients With Stage II and III Colon Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 May 3;2(5):e194154. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.4154. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31099875 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A pragmatic, single-arm clinical trial of a dose modification algorithm for preventing cytopenia-related delays during FOLFOX chemotherapy.Support Care Cancer. 2025 Aug 8;33(9):769. doi: 10.1007/s00520-025-09784-0. Support Care Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40779182 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of resistance training on inflammatory biomarkers and associations with treatment outcomes in colon cancer.Cancer. 2025 May 1;131(9):e35865. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35865. Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40278841 Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary quality and chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in colon cancer.Cancer. 2025 Jan 1;131(1):e35599. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35599. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39369275 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, Topham C, Zaninelli M, Clingan P, Bridgewater J, Tabah-Fisch I, de Gramont A, Multicenter International Study of Oxaliplatin/5-Fluorouracil/Leucovorin in the Adjuvant Treatment of Colon Cancer I (2004) Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 350 (23):2343–2351. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa032709 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Webster-Clark M, Keil AP, Robert N, Frytak JR, Boyd M, Sturmer T, Sanoff H, Westreich D, Lund JL (2022) Comparing Trial and Real-world Adjuvant Oxaliplatin Delivery in Patients With Stage III Colon Cancer Using a Longitudinal Cumulative Dose. JAMA Oncol 8 (12):1821–1824. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.4445 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zok J, Bienkowski M, Radecka B, Korniluk J, Adamowicz K, Duchnowska R (2021) Impact of relative dose intensity of oxaliplatin in adjuvant therapy among stage III colon cancer patients on early recurrence: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Cancer 21 (1):529. doi:10.1186/s12885-021-08183-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

