Astrocytes in selective vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease
- PMID: 38521710
- PMCID: PMC11006581
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tins.2024.02.008
Astrocytes in selective vulnerability to neurodegenerative disease
Abstract
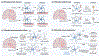
Selective vulnerability of specific brain regions and cell populations is a hallmark of neurodegenerative disorders. Mechanisms of selective vulnerability involve neuronal heterogeneity, functional specializations, and differential sensitivities to stressors and pathogenic factors. In this review we discuss the growing body of literature suggesting that, like neurons, astrocytes are heterogeneous and specialized, respond to and integrate diverse inputs, and induce selective effects on brain function. In disease, astrocytes undergo specific, context-dependent changes that promote different pathogenic trajectories and functional outcomes. We propose that astrocytes contribute to selective vulnerability through maladaptive transitions to context-divergent phenotypes that impair specific brain regions and functions. Further studies on the multifaceted roles of astrocytes in disease may provide new therapeutic approaches to enhance resilience against neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: dementia; glia; heterogeneity; neuropathology; proteinopathy; resilience.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests in relation to this work.
Figures
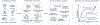

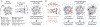
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

