Maternal RNA transcription in Dlk1-Dio3 domain is critical for proper development of the mouse placental vasculature
- PMID: 38521877
- PMCID: PMC10960817
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-06038-3
Maternal RNA transcription in Dlk1-Dio3 domain is critical for proper development of the mouse placental vasculature
Abstract
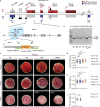
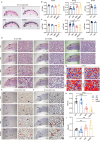
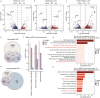
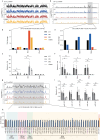
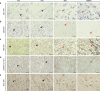
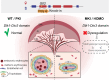
The placenta is a unique organ for ensuring normal embryonic growth in the uterine. Here, we found that maternal RNA transcription in Dlk1-Dio3 imprinted domain is essential for placentation. PolyA signals were inserted into Gtl2 to establish a mouse model to prevent the expression of maternal RNAs in the domain. The maternal allele knock-in (MKI) and homozygous (HOMO) placentas showed an expanded junctional zone, reduced labyrinth and poor vasculature impacting both fetal and maternal blood spaces. The MKI and HOMO models displayed dysregulated gene expression in the Dlk1-Dio3 domain. In situ hybridization detected Dlk1, Gtl2, Rtl1, miR-127 and Rian dysregulated in the labyrinth vasculature. MKI and HOMO induced Dlk1 to lose imprinting, and DNA methylation changes of IG-DMR and Gtl2-DMR, leading to abnormal gene expression, while the above changes didn't occur in paternal allele knock-in placentas. These findings demonstrate that maternal RNAs in the Dlk1-Dio3 domain are involved in placental vasculature, regulating gene expression, imprinting status and DNA methylation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Silencing of maternally expressed RNAs in Dlk1-Dio3 domain causes fatal vascular injury in the fetal liver.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 9;81(1):429. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05462-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39382697 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of Meg8-DMR Enhances Migration and Invasion of MLTC-1 Depending on the CTCF Binding Sites.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 8;23(15):8828. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158828. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955961 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-specific histone modifications regulate expression of the Dlk1-Gtl2 imprinted domain.Genomics. 2007 Feb;89(2):280-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2006.10.005. Epub 2006 Nov 27. Genomics. 2007. PMID: 17126526 Free PMC article.
-
[Review on the genomic imprinting at the mammalian DLK1-DIO3 cluster.].Yi Chuan. 2010 Aug;32(8):769-78. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2010.00769. Yi Chuan. 2010. PMID: 20709673 Review. Chinese.
-
The microRNAs within the DLK1-DIO3 genomic region: involvement in disease pathogenesis.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Mar;70(5):795-814. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1080-8. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22825660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Silencing of maternally expressed RNAs in Dlk1-Dio3 domain causes fatal vascular injury in the fetal liver.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Oct 9;81(1):429. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05462-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39382697 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNAs in the Dlk1-Dio3 Domain Are Essential for Mid-Embryonic Heart Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 26;25(15):8184. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158184. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125754 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

