Real-world effects of novel androgen receptor axis-targeted agents on oncological outcomes in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A multi-institutional retrospective study
- PMID: 38523900
- PMCID: PMC10960088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.prnil.2023.12.002
Real-world effects of novel androgen receptor axis-targeted agents on oncological outcomes in non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A multi-institutional retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The benefits of novel androgen receptor axis-targeted agents (ARATs) on oncological outcomes in patients with non-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (nmCRPC) in real-world settings are unclear.
Methods: This multi-institutional retrospective study included 178 patients with nmCRPC treated between September 2003 and August 2022. Patients were divided into two groups: those who were treated with any novel ARATs, including apalutamide, enzalutamide, darolutamide, and abiraterone acetate, during any line of nmCRPC treatment (novel ARATs group) and those who were not (control group). Multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression analyses were performed to evaluate the effects of novel ARATs on metastasis-free survival (MFS) and overall survival (OS).
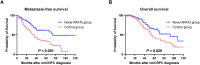
Results: The median age and follow-up period after nmCRPC diagnosis were 76 years and 37 months, respectively. Of the 178 patients, 122 (69%) were treated with novel ARATs after nmCRPC diagnosis. The MFS and OS in the novel ARATs group were significantly longer than those in the control group (P < 0.001 and P = 0.020, respectively). In multivariable analyses, a prostate-specific antigen doubling time (PSADT) of <3 months and novel ARATs were independently and significantly associated with MFS and OS. The effects of novel ARATs on MFS were consistently observed across subgroups stratified by age (<75 years or ≥75 years), history of radical treatment (no or yes), biopsy Gleason score (<9 or ≥9), clinical stage (≤cT3 and cN0, or cT4 or cN1), and PSADT (≥3 months or <3 months).
Conclusion: Novel ARATs were significantly associated with improved oncological outcomes in patients with nmCRPC in a real-world setting, regardless of tumor aggressiveness.
Keywords: Novel ARATs; Oncological outcomes; PSA doubling time; Real-world; nmCRPC.
© 2024 The Asian Pacific Prostate Society. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Zumsteg Z.S., Spratt D.E., Romesser P.B., Pei X., Zhang Z., Polkinghorn W., et al. The natural history and predictors of outcome following biochemical relapse in the dose escalation era for prostate cancer patients undergoing definitive external beam radiotherapy. Eur Urol. 2015;67:1009–1016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boorjian S.A., Thompson R.H., Tollefson M.K., Rangel L.J., Bergstralh E.J., Blute M.L., et al. Long-term risk of clinical progression after biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy: the impact of time from surgery to recurrence. Eur Urol. 2011;59:893–899. - PubMed
-
- Kluth L.A., Shariat S.F., Kratzik C., Tagawa S., Sonpavde G., Rieken M., et al. The hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis and prostate cancer: implications for androgen deprivation therapy. World J Urol. 2014;32:669–676. - PubMed
-
- Mateo J., Fizazi K., Gillessen S., Heidenreich A., Perez-Lopez R., Oyen W.J.G., et al. Managing nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2019;75:285–293. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
