Ultrasound radiomics-based artificial intelligence model to assist in the differential diagnosis of ovarian endometrioma and ovarian dermoid cyst
- PMID: 38523908
- PMCID: PMC10957533
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1362588
Ultrasound radiomics-based artificial intelligence model to assist in the differential diagnosis of ovarian endometrioma and ovarian dermoid cyst
Abstract
Background: Accurately differentiating between ovarian endometrioma and ovarian dermoid cyst is of clinical significance. However, the ultrasound appearance of these two diseases is variable, occasionally causing confusion and overlap with each other. This study aimed to develop a diagnostic classification model based on ultrasound radiomics to intelligently distinguish and diagnose the two diseases.
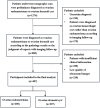
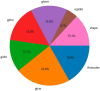
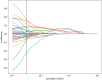
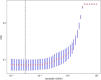
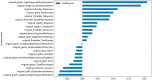
Methods: We collected ovarian ultrasound images from participants diagnosed as patients with ovarian endometrioma or ovarian dermoid cyst. Feature extraction and selection were performed using the Mann-Whitney U-test, Spearman correlation analysis, and the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression. We then input the final features into the machine learning classifiers for model construction. A nomogram was established by combining the radiomic signature and clinical signature.
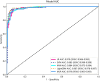
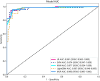
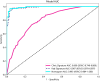
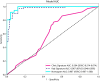
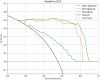
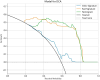
Results: A total of 407 participants with 407 lesions were included and categorized into the ovarian endometriomas group (n = 200) and the dermoid cyst group (n = 207). In the test cohort, Logistic Regression (LR) achieved the highest area under curve (AUC) value (0.981, 95% CI: 0.963-1.000), the highest accuracy (94.8%), and the highest sensitivity (95.5%), while LightGBM achieved the highest specificity (97.1%). A nomogram incorporating both clinical features and radiomic features achieved the highest level of performance (AUC: 0.987, 95% CI: 0.967-1.000, accuracy: 95.1%, sensitivity: 88.0%, specificity: 100.0%, PPV: 100.0%, NPV: 88.0%, precision: 93.6%). No statistical difference in diagnostic performance was observed between the radiomic model and the nomogram (P > 0.05). The diagnostic indexes of radiomic model were comparable to that of senior radiologists and superior to that of junior radiologist. The diagnostic performance of junior radiologists significantly improved with the assistance of the model.
Conclusion: This ultrasound radiomics-based model demonstrated superior diagnostic performance compared to those of junior radiologists and comparable diagnostic performance to those of senior radiologists, and it has the potential to enhance the diagnostic performance of junior radiologists.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; machine learning; ovarian dermoid cyst; ovarian endometrioma; ultrasound radiomics.
Copyright © 2024 Liu, Cai, Zhou, Tian, Wu, Zhang, Yue and Hao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

